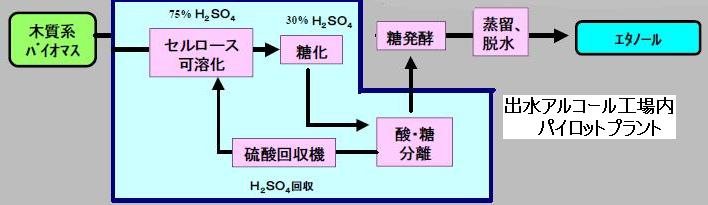
擔杮宱嵪怴暦丂2006/5/11
暷僄僞僲乕儖嶻嬈奼戝丂姅幃岞奐偱帒嬥挷払丂惛惢強寶愝儔僢僔儏
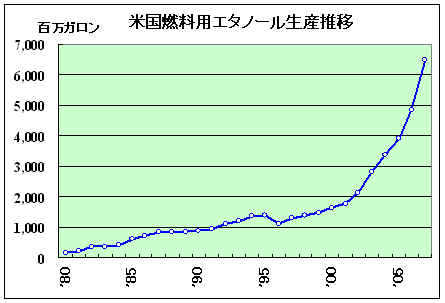
丂慡暷奺抧偱惛惢強偺寶愝儔僢僔儏偑巒傑偭偨丅僯儏乕儓乕僋廈偱偼廈惌晎偑俇侽侽枩僪儖傪曗彆偟壞偐傜寶愝偵拝庤偡傞傎偐丄尨椏偺僩僂儌儘僐僔偺庡梫惗嶻抧偱偁傞僀儕僲僀丄僀儞僨傿傾僫側偳拞惣晹偱妶敪偩丅嬈奅抍懱偺暷嵞惗擱椏嫤夛偵傛傞偲丄寶愝拞偺俁俆僇強傪壛偊傞偲栺侾俁侽僇強偵側傝丄堦楢偺怴憹愝偑廔傢傞棃擭敿偽偵偼擭娫惗嶻擻椡偼嶐擭枛帪揰偺係俁壄僈儘儞偐傜俇俈壄僈儘儞偵憹偊傞尒崬傒丅
丂暷偺栺係暘偺侾傪惗嶻偡傞嵟戝庤傾乕僠儍乕丒僟僯僄儖僘丒儈僢僪儔儞僪(ADM)偼擾嶌暔偺壛岺偑拞怱偩偭偨偑丄僄僞僲乕儖傪拞怱偲偡傞僄僱儖僊乕婇嬈傊偲曄恎偟偮偮偁傞丅嵟嬤丄暷愇桘戝庤僔僃僽儘儞偐傜僷僩儕僔傾丒僂僅儖僣忋媺暃幮挿傪嵟崅宱塩愑擟幰(CEO)偵寎偊偨丅
丂惗嶻検俀埵偺儀儔僒儞僄僫僕乕丄俁埵偺傾儀儞僥傿儞丒儕僯儏乕傾僽儖丒僄僫僕乕偼愭寧丄憡師偄偱暷徹寯庢堷埾堳夛(SEC)偵姅幃偺怴婯岞奐傪怽惪偟偨丅偦傟偧傟侾壄俆愮枩僪儖丄俆愮枩僪儖傪挷払偟丄惛惢強偺寶愝帒嬥偵廩偰傞丅
丂
僄僞僲乕儖娭惻丂暷偱寉尭嶔専摙傕丂僈僜儕儞崅梷惂婜懸
丂暷崙偺桝擖偺戝敿傪愯傔傞僽儔僕儖嶻僄僞僲乕儖偵偼侾僈儘儞摉偨傝54僙儞僩偺娭惻偑偐偐傞丅僽儔僕儖偺僄僞僲乕儖偼僒僩僂僉價偐傜庡偵嶌傜傟傞偑丄暷崙嶻僄僞僲乕儖偺尨椏偼僩僂儌儘僐僔丅暷崙偺娭惻偵偼惌帯揑偵傕堦掕偺塭嬁椡傪帩偮傾僀僆儚丄僀儕僲僀椉廈側偳偺僩僂儌儘僐僔擾壠傪曐岇偡傞慱偄偑偁傞丅
暷崙丂僄僞僲乕儖擻椡丂乮昐枩僈儘儞乯2006/1 RFU
http://www.ethanolrfa.org/objects/pdf/outlook/outlook_2006.pdf
| 丂 | 憖嬈拞 | 寶愝丒 憹愝拞 |
Archer Daniels Midland |
1,070 |
- |
VeraSun Energy |
230 |
- |
Aventine Renewable Energy |
150 |
57 |
Advanced Bioenergy |
- |
100 |
ASAlliacnes Biofuels |
- |
200 |
Hawkeye Renewables |
50 |
150 |
Midwest Grain Processors |
50 |
102 |
New Energy |
102 |
- |
US BioEnergy |
- |
145 |
| 偦偺懠 | 丂 | 丂 |
崌寁 |
4,336 |
1,981 |
2005 World Ethanol
Production - All grades, in millions of gallons丂Source: F.O. Licht
USA 4264丂Brazil 4227丂China 1004丂India 449丂France 240丂Russia 198丂South Africa 103丂Germany 114
Total 12150
Archer Daniels Midland
暷僇乕僊儖(旕忋応)偵師偖暷崙戞2埵偺崚暔彜幮丅2002擭丄僄僞僲乕儖惗嶻偱嫞崌偟偰偄偨儈僱僜僞丒僐乕儞丒僾儘僙僢僒乕僘(俵俠俹)傪攦廂偟丄摨帠嬈偱暷崙庱埵偺抧埵傪屌傔偨丅2006擭5寧丄尦僔僃僽儘儞忋媺暃幮挿偺僷僩儕僔傾丒僂僅儖僣傪俠俤俷偵彽阗偟丄僄僱儖僊乕娭楢帠嬈嫮壔傪恾傞丅
Corn processor merges with ADM丂2002/7/12
Minnesota Corn Processors LLC has agreed to merge with a subsidiary of agribusiness giant Archer Daniels Midland in a move that would bolster ADM's market-leading ethanol production capacity.
MCP was ADM's chief competitor in the ethanol market, and the combined companies would control almost half the US production of ethanol. This hefty market share could benefit from a recently passed Senate energy bill which calls for a tripling in US ethanol production over the next decade.
MCP also produces corn sweeteners and starch products for sale in the beverage and food industries, and owns and operates 19 corn sweetener distribution terminals nationwide.
The company also produces starches for sale to the paper industry, as well as feed products.
VeraSun Energy
僒僂僗僟僐僞廈偵杮嫆抧傪峔偊傞摨幮偼丄僩僂儌儘僐僔偐傜僄僞僲乕儖傪惢憿偡傞婇嬈偩丅僄僞僲乕儖偼傾儖僐乕儖
偺堦庬偱丄懠偺嵽椏偲崿偤偰擱椏偲偟偰棙梡偟偨傝丄堦晹偱偼幵偺庡擱椏偲偟偰巊傢傟偰偄傞丅摨幮偼尰嵼丄擭娫2壄3000枩僈儘儞乮栺8壄7000枩儕僢僩儖乯傪惗嶻偟偰偄傞丅寁夋抜奒偵偁傞岺応偑姰惉偡傟偽丄2007擭偵偼擭娫3壄4000枩僈儘儞乮12壄9000枩儕僢僩儖乯丄2008擭戞1巐敿婜偵偼5壄6000枩僈儘儞乮栺21壄2000枩儕僢僩儖乯惗嶻偱偒傞傛偆偵側傞丅
Aventine
Renewable Energy, Inc.
Aventine
Renewable Energy, Inc. supplies more than 500 million gallons of
the nation's growing ethanol needs as a leading producer and
marketer of ethanol in the United States.
In 1998, Aventine Renewable Energy, Inc. began its bio-products
division to produce dried brewer's yeast and other value added
products. Aventine Renewable Energy, Inc. supplies much of the
nation's ethanol needs through its wholly-owned plant in Pekin,
IL, partially-owned Nebraska Energy plant in Aurora, NE, and
business relationships and marketing alliances.
Pacific Ethanol, Inc.
2005擭3寧丄幮柤傪傾僋僙僔僥傿偐傜尰幮柤傊曄峏丅摨擭11寧丄儅僀僋儘僜僼僩偺價儖丒僎僀僣夛挿偺屄恖搳帒婎嬥僇僗働乕僪丒僀儞儀僗僩儊儞僩偑8400枩僪儖傪搳偠偰丄晛捠姅1050枩姅偵揮姺壜擻側桪愭姅傪庢摼偟偨偙偲偐傜拲栚偝傟偨丅帒嬥挷払偺栚揑偼暷惣奀娸偱偺擱椏揧壛嵻岺応寶愝丅
價儖丒僎僀僣偺摨幮帩姅斾棪偼28亾偲側傞丅
2005 擭僄僱儖僊乕惌嶔朄偺梫巪
僽僢僔儏戝摑椞偑堦斒嫵彂墘愢(2006/1/31)偱帵 偟偨愭恑揑僄僱儖僊乕丒僀僯僔傾僥傿僽偺梫巪
侾丏壠掚偲婇嬈偵偍偗傞僄僱儖僊乕尮偺抲偒姺偊 嵞惗壜擻擱椏嫤夛(俼俥俙亖Renewable Fuels Association)庡嵜偺夛媍(4/25)偵偍 偗傞僽僢僔儏戝摑椞偺墘愢偺梫巪
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
US' Archer Daniels
Midland to build new ethanol plant in Iowa
Large US ethanol producer Archer Daniels Midland will build a dry
corn milling plant with an annual capacity of 275 million gallons
in Cedar Rapids, Iowa, as part of a two-step project to boost its
output of the gasoline additive, the company said Wednesday.
挬擔怴暦丂2006/6/12
僈僜儕儞丄僶僀僆僄僞僲乕儖崿崌偵揮姺丂俁侽擭傑偱
丂娐嫬徣偼丄崙撪偱巊梡偝傟傞帺摦幵偺僈僜儕儞偺慡検傪丄俀侽俁侽擭傑偱偵怉暔帒尮偐傜偮偔傞僶僀僆僄僞僲乕儖侾侽亾崿崌乮俤侾侽乯偵愗傝懼偊傞曽恓傪寛傔偨丅嫗搒媍掕彂偺栺懇婜娫乮侽俉乣侾俀擭乯偵丄僈僜儕儞幵偺怴幵偡傋偰傪俤侾侽懳墳偲偡傞偨傔偺娭學朄椷傕惍旛偡傞丅俆寧枛偺乽怴丒崙壠僄僱儖僊乕愴棯乿偱塣桝僄僱儖僊乕偺扙愇桘壔傪懪偪弌偟偨宱嵪嶻嬈徣偲楢実偟丄棃擭偵傕尒捈偡嫗搒媍掕彂栚昗払惉寁夋偵惌晎曽恓偲偟偰惙傝崬傓丅
丂寁夋偱偼傑偢丄栺懇婜娫拞偵丄僈僜儕儞廀梫偺嵟戝俀暘偺侾掱搙傪俁亾崿崌偝偣偨僈僜儕儞乮俤俁乯偵愗傝懼偊傞丅俀侽擭偵偼俤侾侽偺嫙媼傪巒傔丄俁侽擭偵偼慡検偺俤侾侽壔傪栚巜偡丅偙傟偵敽偆俠俷俀嶍尭検偼慡検揮姺帪傑偱偵栺侾愮枩僩儞偲帋嶼丅俁侽擭帪揰偺僶僀僆僄僞僲乕儖摫擖検偼丄尨桘姺嶼偱俀俀侽枩僉儘儕僢僩儖傪尒崬傓丅
2006/06/20 擔婗
暷崙偱僶僀僆僄僞僲乕儖惗嶻帠嬈偵嶲夋
-- 攑栘嵽尨椏僄僞僲乕儖惗嶻偺帠嬈奐敪婎杮嫤掕傪掲寢
--
丂擔婗姅幃夛幮(戙昞庢掲栶夛挿寭CEO 廳媣媑峅丄墶昹杮幮
墶昹巗惣嬫傒側偲傒傜偄2-3-1)偼丄暷崙偱攑栘嵽傪尨椏偲偡傞帺摦幵擱椏梡僶僀僆僄僞僲乕儖惢憿丒斕攧帠嬈傪幚巤偡傞偨傔丄偙偺傎偳暷崙偺帠嬈僷乕僩僫乕偲偺娫偱帠嬈奐敪婎杮嫤掕傪掲寢偟傑偟偨偺偱偍抦傜偣偟傑偡丅帠嬈寁夋偺徻嵶偼埲壓偺捠傝偱偡丅
| 1. | 帠嬈僷乕僩僫乕 | 丗 | 暷崙傾儖働僲乕儖幮(Arkenol, Inc. 杮幮丗僇儕僼僅儖僯傾廈) |
| 2. | 嫤掕撪梕 丂丂丂丂丂 | 丗 | 崱屻暷崙撪偵擔婗丄傾儖働僲乕儖幮側偳偑弌帒偡傞怴帠嬈夛幮傪愝棫偟丄摨崙撪偱攑婞暔張棟 偝傟偰偄傞攑栘嵽傪尨椏偲偡傞擭嶻栺3枩僉儘儕僢僩儖偺僶僀僆僄僞僲乕儖傪惗嶻偟丄斕攧偡傞 |
| 3. | 帠嬈抧 | 丗 | 暷崙僇儕僼僅儖僯傾廈僆儗儞僕孲 |
| 4. | 摉幮偺栶妱 | 丗 | [1]
僶僀僆僄僞僲乕儖偵娭偡傞惢憿媄弍丒僲僂僴僂丄僾儘僙僗愝寁僷僢働乕僕偺採嫙
[2] 帠嬈夛幮傊偺帒嬥搳帒 [3] 愝旛偺塣揮丒曐庣偵娭傢傞媄弍僒乕價僗採嫙 |
| 5. | 帠嬈僗働僕儏乕儖 | 丗 | [1]
僾儘僙僗愝寁偺姰惉 2006擭拞
[2] 帠嬈夛幮愝棫丄愝旛寶愝(EPC)奐巒 2007擭弶摢 [3] 愝旛姰惉丄僄僞僲乕儖惗嶻奐巒 2009擭弶摢 |
丂摉幮偼埲慜傛傝擾嶌暔偺宻傗恈丄攑栘嵽側偳偺栘幙宯巆熢摍僶僀僆儅僗帒尮偺擱椏壔媄弍偵拝栚偟丄傾儖働僲乕儖幮偲偺撈愯採実偵傛傝摨幮偑強桳偡傞僶僀僆僄僞僲乕儖惢憿摿嫋媄弍偺彜嬈壔幚徹尋媶傪懕偗偰偒傑偟偨丅2002擭偵偼幁帣搰導弌悈巗偺(撈)怴僄僱儖僊乕丒嶻嬈媄弍憤崌奐敪婡峔(NEDO)弌悈傾儖僐乕儖岺応撪偵丄NEDO偺埾戸帠嬈偲偟偰僷僀儘僢僩僾儔儞僩(幚徹憰抲)傪寶愝偟丄摉幮偑帩偮僾儘僙僗媄弍丒奐敪媄弍偺岺嬈壔僲僂僴僂傪慻傒崌傢偣傞偙偲偱杮媄弍偺彜嬈壔傊偺媄弍拁愊傪峴側偭偰偒傑偟偨丅

擔杮宱嵪怴暦丂2006/6/24
丂丂丂丂丂丂丂丂丂丂丂丂丂丂僙儖儘乕僗偐傜偺僄僞僲乕儖
墷廈愇桘戝庤丂僶僀僆擱椏搳帒杮奿壔
丂BP丄媄弍奐敪偵5壄僪儖
丂僔僃儖墷暷偱検嶻懱惂
丂BP偼僶僀僆媄弍偵桪傟傞塸暷偺桳椡戝妛偲採実丄僶僀僆擱椏奐敪偺愱栧尋媶強傪憂愝偡傞丅怉暔尨椏偐傜僶僀僆擱椏傊偺岠棪揑側惗嶻媄弍傗擱椏偵揮姺偱偒傞怴偨側怉暔偺尋媶傪媫偖丅僕儑儞丒僽儔僂儞幮挿偼乽堛栻昳暘栰傪戝偒偔曄偊偨僶僀僆媄弍偼僄僱儖僊乕暘栰偱傕廳梫側栶妱傪壥偨偡乿偲嫮挷偡傞丅
丂BP偼嶐擭丄懢梲岝傗晽椡偺敪揹側偳戙懼僄僱儖僊乕暘栰偵侾侽擭娫偱俉侽壄僪儖傪搳帒偡傞寁夋傪寛掕偟偨丅崱夞偺僶僀僆擱椏傊偺搳帒偼捛壛埬審偱丄僶僀僆擱椏偺尋媶偩偗偱俆壄僪儖偺搳帒偼僄僱儖僊乕嬈奅偱嵟戝婯柾偩丅俀侽擔偵偼暷僨儏億儞偲僶僀僆擱椏偺検嶻側偳偺帠嬈壔偱採実偡傞偙偲傕敪昞偟偨丅
丂僔僃儖偼僇僫僟偺僶僀僆擱椏戝庤婇嬈偱偁傞僀僲僎儞乮惓偟偔偼
Iogen)偲墷暷偱崌曎惗嶻偵忔傝弌偡曽恓偩丅僀僲僎儞偼僩僂儌儘僐僔偺宻側偳怉暔偺旕怘梡晹暘傪擱椏偵揮姺偡傞媄弍傪帩偪丄掅僐僗僩偺惗嶻偑壜擻丅僔僃儖偼俀侽侽俈擭偵傕僀僲僎儞偑杒暷偱寶愝偡傞検嶻岺応偵搳帒偟丄擭侾丏俆壄亅俀壄儕僢僩儖偺惗嶻暘偺戝敿傪帺幮岦偗偵挷払偡傞峫偊偩丅僀僲僎儞偲偼墷廈岺応偺怴愝偱傕嫤椡偡傞丅
丂僗儁僀儞偺愇桘戝庤儗僾僜儖YPF偼壠掚偺攑怘桘側偳偐傜惗嶻偡傞僶僀僆僨傿乕僛儖擱椏偱悽奅嵟戝婯柾偺惗嶻嫆揰傪寶愝偡傞丅侽俋擭傑偱偵俁壄儐乕儘(係係侽壄墌)傪搳帒偟丄僗儁僀儞撪偵俇僇強偺岺応傪棫偪忋偘傞丅墷廈偱偼怴幵搊榐戜悢偺傎傏俆妱偑僨傿乕僛儖幵偱丄愽嵼廀梫偼戝偒偄偲敾抐偟偨丅
BP Pledges $500 Million for Energy Biosciences
Institute and Plans New Business to Exploit Research
http://www.bp.com/genericarticle.do?categoryId=2012968&contentId=7018719
As part of its continuing drive to find longer term
commercial alternatives to oil and gas, BP is to fund radical
research aimed at probing the emerging secrets of bioscience and
applying them to the production of new and cleaner energy,
principally fuels for road transport.
The company plans to spend
$500 million over the next ten years to
establish a dedicated biosciences energy research laboratory
attached to a major academic centre in the US or UK, the first
facility of its kind in the world.
Chief executive Lord Browne said BP had begun discussions with
several leading universities to identify which could host the BP Energy Biosciences Institute (EBI),
with the aim of launching early research programmes by the end of
2007.
BP Forms BP Alternative
Energy 丂
http://www.bp.com/genericarticle.do?categoryId=2012968&contentId=7012352
BP today announced that
it plans to double its investment in alternative and renewable
energies to create a new low-carbon power business with the
growth potential to deliver revenues of around $6 billion a year
within the next decade.
Building on the
success of BP Solar - which expects to hit revenues of $1 billion
in 2008 - BP Alternative Energy will manage an investment
programme in solar, wind, hydrogen and
combined-cycle-gas-turbine (CCGT) power generation, which could amount to $8 billion over
the next ten years.
CCGT 暋崌僒僀僋儖僈僗僞乕價儞:
In a CCGT plant, a gas turbine generator generates electricity and the waste heat from the gas turbine is used to make steam to generate additional electricity via a steam turbine, this last step enhances the efficiency of electricity generation. Most new gas power plants are of this type.
Browne said the first
phase of investment would total some $1.8 billion over
the next three years,
spread in broadly equal proportions between solar, wind, hydrogen
and CCGT power generation. Investment will be made step by step,
and will depend on the nature of opportunities and their
profitability.
BP currently has
more than 100 megawatts of solar
manufacturing capacity in the US, Spain, India and
Australia, with a plan to double its capacity before the end of
next year. BP recently signed a strategic joint venture to access
China乫s expanding solar market and
provide local manufacturing capacity and is exploring similar
opportunities elsewhere in the region.
Investment in hydrogen fuels will include the world乫s first commercial project - at
Peterhead, in Scotland - to turn natural gas into hydrogen by
stripping out carbon dioxide and pumping it into depleted oil
reservoirs.
The hydrogen will
be used at a power station in Peterhead to generate 350 megawatts
of 乪clean乫 electricity, and the carbon
dioxide re-injected into the offshore Miller field. BP is looking
at a similar sequestration scheme to make hydrogen from low-value
coke by-products at a US refinery which would be used to generate
500 megawatts at an adjacent new-build power plant.
Investment
projected for wind represents a significant step up
in this area of power generation for BP. The company currently
runs two wind farms alongside existing oil plants in the
Netherlands. It also owns industrial land in open, high-wind
regions of the US, away from residential areas, providing the
possibility to build the first large-scale US wind farm
generating up to 200 megawatts in 2007. The company has
identified enough US sites to accommodate wind turbines with a
total capacity of 2,000 megawatts.
Projected
investment in CCGT will be spent mainly in the US
where the company already has significant co-generation capacity
and is currently finalising plans for a new $400 million scheme
at one of its major plants that will deliver 100 megawatts of
power to the plant, and 420 megawatts to the local electricity
grid.
BP Alternative
Energy will be based in Sunbury, Middlesex and initially employ
some 2,500 people around the world. It will be headed by Steve
Westwell, reporting to Vivienne Cox, chief executive of BP乫s Gas, Power & Renewables
division.
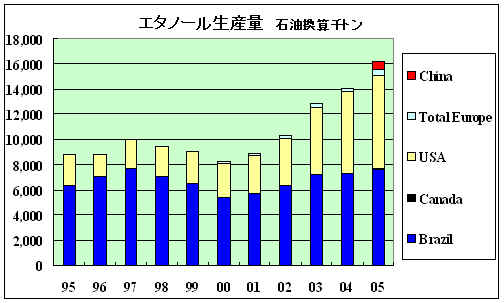
Renewable
energy- ethanol
Production (Thousand tonnes of oil
equivalent)
| 丂 | 1995丂 | 1996丂 | 1997丂 | 1998丂 | 1999丂 | 2000丂 | 2001丂 | 2002丂 | 2003丂 | 2004丂 | 2005丂 |
Brazil |
6,365 |
7,058 |
7,737 |
7,052 |
6,483 |
5,343 |
5,726 |
6,286 |
7,226 |
7,314 |
7,563 |
Canada |
n/a |
n/a |
n/a |
n/a |
n/a |
n/a |
n/a |
n/a |
n/a |
n/a |
130 |
USA |
2,438 |
1,761 |
2,280 |
2,426 |
2,574 |
2,793 |
3,022 |
3,779 |
5,309 |
6,435 |
7,380 |
Total Europe |
n/a |
n/a |
n/a |
n/a |
n/a |
120 |
136 |
245 |
268 |
266 |
454 |
Australia |
n/a |
n/a |
n/a |
n/a |
n/a |
n/a |
n/a |
n/a |
37 |
14 |
11 |
China |
n/a |
n/a |
n/a |
n/a |
n/a |
n/a |
n/a |
n/a |
n/a |
n/a |
643 |
TOTAL WORLD |
8,803 |
8,818 |
10,016 |
9,478 |
9,057 |
8,256 |
8,884 |
10,310 |
12,840 |
14,030 |
16,182 |
About Iogen 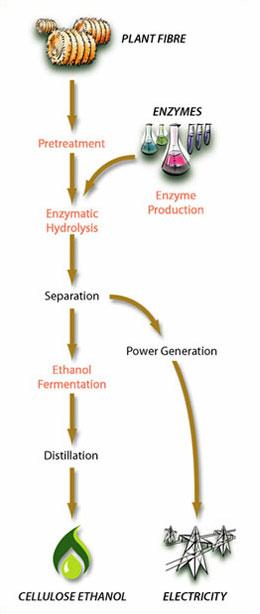
http://www.iogen.ca/
Established in the 1970s,
Iogen Corporation has become one of Canada's leading
biotechnology firms. Iogen is an industrial manufacturer of
enzyme products with a focus on products for use by the pulp and
paper, textile and animal feed industries. It also is the world
leader in technology to produce cellulose ethanol, a fully renewable, advanced
biofuel that can be used in today's cars.
Iogen is a privately held company, based in Ottawa, Ontario,
Canada, with a rapidly growing work force. Public and private
investment in Iogen has totaled approximately $130 million over
the past 25 years. Major investors include the
Royal Dutch/Shell Group, Petro-Canada and the Government
of Canada.
Iogen employs a staff of approximately 180 people, with over half
involved in research and development, and engineering; one fifth
in manufacturing; and the balance in sales, marketing, and
administration.
Cellulose ethanol can
significantly:
丒lower
overall greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions
丒reduce
reliance on imported oil and increase energy security
丒help
build rural economies and improve farm income
Cellulose ethanol is one of the most cost effective ways to
reduce GHGs and gasoline consumption in road transport and can
deliver benefits similar to improved vehicle efficiency.
Iogen built and operates the world's only demonstration scale
facility to convert biomass to cellulose ethanol using enzyme
technology. This facility is located in Ottawa. Iogen is
currently assessing potential locations for the world's first
commercial prototype cellulose ethanol plant.
In the long-term, Iogen intends to commercialize its cellulose
ethanol process by licensing its technology broadly through
turnkey plant construction partnerships. License fees and the
supply of enzymes to the licensees' plants will generate income.
Partners
Iogen has several partners that benefit from the company丩s enzyme expertise. Active research and business relationships include:
The Royal Dutch/Shell Group
In 2002, after a worldwide search for the leading options in biofuels, Royal Dutch/Shell Group selected Iogen as a development partner. Shell invested C$46 million in Iogen, and the two companies are cooperating on commercialization. Shell is one of the world's largest integrated oil companies, and is committed to expanding its sustainable development practices.
Goldman Sachs & Co
In 2006, Goldman Sachs & Co. of New York became the first major Wall Street firm to make a commitment to cellulose ethanol by investing C$30 million in Iogen乫s cellulose ethanol technology, giving it a minority stake in Iogen. The funds will be used to accelerate Iogen乫s commercialization program. Goldman Sachs & Co. is a leading global investment banking, securities and investment management firm and is a leading investor in renewable and alternative energy.
Petro-Canada
In 1997, Petro-Canada signed a partnership with Iogen to further develop cellulose ethanol technology. With a $15.8 million investment from Petro-Canada, Iogen built the company's pre-commercial demonstration plant. In December 2003, Petro-Canada extended it's investment in Iogen丩s EcoEthanol? program. Petro-Canada is one of Canada's largest integrated oil companies.
Government of Canada
The Government of Canada has been a development partner of Iogen's for several years through different Canadian federal government departments. These include the National Research Council (NRC), Natural Resources Canada (NRCAN), and Technology Partnerships Canada (TPC). Iogen partnered with the NRC in 1994 to develop unique enzymes for the pulp and paper industry. In April 1997, Iogen released the world's first improved xylanase using biotechnology for pulp bleaching. In January 1999, Iogen entered into a partnership with TPC and secured a $10-million loan to help build its ethanol demonstration facility in Ottawa.
DSM
Since 1991, DSM (formerly Roche Vitamins) has had a supply agreement with Iogen for the exclusive manufacture and distribution of animal feed enzymes sold under the brand name Roxazyme G2. These enzymes enhance the performance of animal feeds in poultry and swine diets. DSM is the world's largest maker of vitamins and a major supplier to the animal feed industry.
2006/1/8丂Volkswagen, Shell and Iogen
Volkswagen, Shell and Iogen to Study Feasibility of Producing Cellulose Ethanol in Germany
Volkswagen, Shell and Iogen Corporation announced today that they will conduct a joint study to assess the economic feasibility of producing cellulose ethanol in Germany. This advanced biofuel produced by Iogen can be used in today乫s cars and can cut CO2 emissions by 90% compared with conventional fuels.
Iogen乫s cellulose ethanol is a fully renewable advanced biofuel made from the non-food portion of agriculture residue such as cereal straws and corn stover, and is one of the most cost-effective ways to reduce greenhouse gas emissions in road transport. Iogen乫s cellulose ethanol technology is the result of more than 25 years of research and development. The company operates the world乫s only cellulose ethanol demonstration-scale facility and made the first commercial shipments of this fuel in April 2004.
Shell乫s Iogen venture now producing
cellulose ethanol fuel
Today, Shell Global Solutions International B.V. confirmed that Iogen Corporation (Iogen), a world-leading
bio-fuels technology company, is successfully producing the world乫s first cellulose ethanol fuel
available for commercial use.
Replacing part of the fossil-derived transportation fuel with
biomass-derived products can be an effective way to reduce carbon
dioxide emissions - thus contributing significantly to
sustainable solutions.
Shell Global Solutions have world-leading expertise in fuel
research, technology implementation, project execution,
manufacturing, distribution and blending. Working together, Shell Global
Solutions and Iogen are combining Shell乫s expertise with Iogen乫s innovative cellulose ethanol
technology
to ensure commercial success for this venture.
Bio-fuels
http://www.shell.com/home/Framework?siteId=royal-en&FC3=/royal-en/html/iwgen/what_we_do/oil_products/biofuels_0316.html&FC2=/royal-en/html/iwgen/what_we_do/oil_products/zzz_lhn.htmlFuel-ethanol is used in large quantities in Brazil, where it is produced from sugar cane, and in the USA, where it is made from corn. Sugar cane may replace well over 10 percent of all gasoline used in tropical regions, where it is grown. Corn and cereals are less productive, more expensive and in competition with the food industry. Greater potential exists in new technologies that convert the cellulose contained in plant residues, such as straw and stems, into sugars. One of the most advanced companies in this field is IOGEN. Shell has formed a partnership with this Canadian-based company, to bring this technology to the benefit of consumers.
Meeting the energy
challenge - Shell乫s commitment to alternative energy
New developments in Biofuels, Wind, Solar and Hydrogen announced
Royal Dutch Shell plc provided an update of its activities in
alternative energy including Biofuels, Wind, Solar and Hydrogen.
Shell has now invested over US$1 billion in alternative
energies,
making it one of the world乫s leading companies in the sector.
In
partnership with Iogen of Canada, cellulose ethanol Biofuels are
being successfully produced from plant waste. By producing Biofuels from
plant waste instead of food crops, the potential stress on the food
chain is alleviated. The Iogen process produces a fuel which can
be used in today's cars, cutting CO2 lifecycle emissions by 90%
compared with conventional fuels. Shell recently announced a
Memorandum of Understanding with Volkswagen and Iogen to explore
the economic feasibility of producing cellulose ethanol in
Germany. Shell Canada has been working with Iogen to develop a viable commercial
framework for a facility in Canada.
These projects complement Shell乫s existing partnership with CHOREN
Industries
of Germany. CHOREN have a patented Biomass-gasification
process that converts biomass - such as woodchips - into
ultra-clean synthetic gas that can then be converted for use
in diesel through Shell乫s Gas- to-Liquids technology.
CHOREN is preparing construction for the world乫s first commercial
biomass-to-liquids facility in Freiberg, Germany.
Wind is currently one of the most
promising sources of renewable energy.
Shell also announced a
Memorandum of Understanding today outlining plans to explore the
potential for wind energy developments in China
in partnership with Guohua Energy Investment Corporation of the
China Shenhua Group, a leading national energy supplier.
In the area of Solar energy, Shell has been progressing the
next generation of technologies, including CIS
乪thin-film乫. Shell believes that non-silicon
based technologies such as CIS are more likely to become
competitive with retail electricity in the coming years. Shell乫s CIS technology is supported by
four years of manufacturing and marketing experience. The
technology recently achieved a 13.5% world record efficiency for
thin-film products, and is supported by International
Electrotechnical Commission certification.
CHOREN 丂http://www.choren.com/en/choren/company/
is one of the world乫s leading gasification technology companies for solid biomass and oil based residue feedstock.
The center-piece of the technology is the patented Carbo-V® process that made the production of tar-free synthetic combustion gas possible and provided the breakthrough for the conversion of biomass to energy.
The Carbo-VR Process is a three-stage gasification process involving the following sub-processes:
丂low temperature gasification,
丂high temperature gasification and
丂endothermic entrained bed gasification.
During the first stage of the process, the biomass (with a water content of 15 - 20 %) is continually carbonized through partial oxidation (low temperature pyrolysis) with air or oxygen at temperatures between 400 and 500 亱C, i.e. it is broken down into a gas containing tar (volatile parts) and solid carbon (char).
During the second stage of the process, the gas containing tar is post-oxidized hypostoichiometrically using air and/or oxygen in a combustion chamber operating above the melting point of the fuel乫s ash to turn it into a hot gasification medium.
During the third stage of the process, the char is ground down into pulverized fuel and is blown into the hot gasification medium. The pulverized fuel and the gasification medium react endothermically in the gasification reactor and are converted into a raw synthesis gas. Once this has been treated in the appropriate manner, it can be used as a combustible gas for generating electricity, steam and heat or as a synthesis gas for producing SunDiesel.
CIS懢梲揹抮偲偼
CIS偲偼庡尨椏偱偁傞摵(Copper)僀儞僕僂儉(Indium)僙儗儞(Selenium)偺摢暥帤傪偲偭偨敄枌宯偺懢梲揹抮偱偡丅
偙偺CIS懢梲揹抮偺摿挿偼埲壓偺4揰偱偡丅
1)廬棃宆偺寢徎僔儕僐儞宯懢梲揹抮偲偼堎側傞慡偔怴偟偄峔憿偺敄枌壔崌暔宯懢梲揹抮偱偡丅
2)僔儕僐儞傪巊梡偟側偄偺偱丄寢徎宯偱婋湝偝傟偰偄傞尨椏晄懌栤戣偵塭嬁偝傟傑偣傫丅
3)墧傗僇僪儈僂儉側偳偺暔幙傪巊梡偟偰偄側偄娐嫬懳墳宆彜昳偱偡丅
4)奜娤偼寢徎宯偲偼堎側傝丄崟堦怓偺棊偪拝偄偨僨僓僀儞偲側偭偰偄傑偡丅
擔杮宱嵪怴暦丂2006/6/25
僄僱儖僊乕偺棟壢丂怉暔帒尮
丂怷椦傪"桘揷"偵曄偊傞丂峺慺偱摐偵暘夝
傾儖僐乕儖擱椏
丂拞崙抧曽偺嶳偁偄丄桯尯側僸僲僉偺怷偵埻傑傟偨恀怴偟偄傾儖僐乕儖岺応偑偁傞丅栘偔偢偐傜僄僞僲乕儖側偳傾儖僐乕儖傪偮偔傞崙撪桞堦偺巤愝偩丅嶰堜憿慏偲怴僄僱儖僊乕丒嶻嬈媄弍憤崌奐敪婡峔(NEDO)偑嶐擭俇寧偵寶愝偟偨嶰堜憿慏恀掚僶僀僆僄僞僲乕儖幚徹僾儔儞僩乮壀嶳導恀掚巗)丅偙偙偱丄怷椦傪"桘揷"偺傛偆側僄僱儖僊乕尮偵曄偊傞憇戝側幚尡偑恑傫偱偄傞丅丂岺応偱偼僸僲僉偺栘偔偢傪棸巁偱張棟偟丄峺慺偺擖偭偨僞儞僋撪偱暘夝偡傞丅栘偔偢惉暘偺傎偲傫偳傪愯傔傞僙儖儘乕僗偼摐偑嵔忬偵挿偔楢側偭偨暘巕峔憿丅峺慺偑僴僒儈偺傛偆偵嵔傪愗傝丄偽傜偽傜偺摐偵偡傞丅
丂偱偒偨摐偼暿偺僞儞僋偱峺曣傪崿偤丄敪峺偝偣偰傾儖僐乕儖偵曄偊傞丅偙偺斀墳偼庰傪憿傞偺偲摨偠偩丅栺係擔偱姡憞廳検侾僩儞偺栘偔偢偑俀俁侽僉儘僌儔儉偺僄僞僲乕儖偵側傞丅偱偒偨僄僞僲乕儖偼僈僜儕儞偵崿偤丄帺摦幵偺擱椏偵巊偭偰偄傞丅
丂偦傕偦傕丄擱椏偵偡傞怉暔帒尮偼戝偒偔俀偮偵暘偐傟傞丅侾偮偼丄嵟弶偐傜丄偱傫傉傫側偳敪峺偑梕堈側摐暘偲偟偰嵦庢偝傟傞晹暘傪巊偆曽朄偱丄僩僂儌儘僐僔側傜幚偺晹暘偵偁偨傞丅尰嵼惙傫側擱椏壔偼傎偲傫偳偑偙傟丅偨偩偟丄怘椏傪傢偞傢偞擱椏偵偟偰偄傞懁柺偑偁傞丅
丂傕偆侾偮偼僙儖儘乕僗傪巊偆曽朄偱丄僩僂儌儘僐僔側傜幉傗梩丄宻偺晹暘丅傎偲傫偳僄僱儖僊乕棙梡偼恑傫偱偄側偄丅偟偐偟丄栘偔偢丄堫傢傜丄敒傢傜丄寶抸攑嵽丄巻偔偢丄壥偰偼嶨憪傑偱丄悽奅偼僙儖儘乕僗偺攑婞暔偱偁傆傟偰偄傞丅側偤丄偁傝梋傞帒尮傪棙梡偟側偄偺偩傠偆偐丅
丂僸儞僩偼儎僊丅恖娫偼巻傪怘傋偰傕徚壔偱偒側偄偑丄儎僊偼巻偺僙儖儘乕僗傪摐偵曄偊丄徚壔偱偒傞丅堓偺拞偵僙儖儘乕僗暘夝峺慺傪曻弌偡傞旝惗暔傪廧傑傢偣偰偄傞偐傜偩丅旝惗暔偺斀墳側傜僄僱儖僊乕偼彮側偄丅嶰堜憿慏側偳偺幚徹僾儔儞僩偺暘夝峺慺傕丄旝惗暔偐傜摼偨傕偺偩丅
丂
July 7, 2006 U.S.
Department of Energy
DOE Publishes
Roadmap for Developing Cleaner Fuels
Research Aimed at
Making Cellulosic Ethanol a Practical Alternative to Gasoline
The U.S. Department
of Energy (DOE) today released an ambitious new research agenda
for the development of cellulosic ethanol as an
alternative to gasoline. The 200-page scientific 乬roadmap乭
cites recent
advances in biotechnology that have made cost-effective
production of ethanol from cellulose, or inedible plant fiber, an
attainable goal. The report outlines a detailed research plan for
developing new technologies to transform cellulosic ethanol?a
renewable, cleaner-burning, and carbon-neutral alternative to
gasoline?into an economically viable transportation fuel.
乬Cellulosic
ethanol has the potential to be a major source for transportation
fuel for America乫s energy future,乭
Under Secretary for
Science Raymond L. Orbach said. 乬Low production cost and high
efficiency require transformational changes in processing
cellulose to ethanol. DOE乫s Genomics: GTL program is poised
to help do just that.乭
The roadmap
responds directly to the goal recently announced by Secretary of
Energy Samuel W. Bodman of displacing 30 percent of 2004
transportation fuel consumption with biofuels by 2030. This goal was set in response to
the President's Advanced Energy Initiative.
The roadmap
identifies the research required for overcoming challenges to the
large-scale production of cellulosic ethanol to help meet this
goal, including maximizing biomass feedstock productivity,
developing better processes by which to break down cellulosic
materials into sugars, and optimizing the fermentation process to
convert sugars to ethanol. Cellulosic ethanol is derived from the
fibrous, woody and generally inedible portions of plant matter
(biomass).
The focus of the
research plan is to use advances in biotechnology -- first
developed in the Human Genome Project and continued in the Genomics: GTL
program in
the Department乫s Office of Science -- to
jump-start a new fuel industry whose products can be transported,
stored and distributed with only modest modifications to the
existing infrastructure and can fuel many of today乫s vehicles.
The new roadmap was
developed during a December 2005 workshop hosted jointly by the
Office of Biological and Environmental Research in the Office of
Science and the Office of the Biomass Program in the Office of
Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy. The success of the plan
relies heavily on the continuation of the partnership between the
two offices established at that workshop.
乬Biofuels
represent a tremendous opportunity to move our nation toward a
reduced dependence on imported oil,乭 DOE Assistant Secretary for Energy
Efficiency and Renewable Energy Alexander Karsner said. 乬We fully intend to use all of our
resources and talent to support the President乫s goal of breaking our addiction
to oil, while also enhancing our energy security.乭
The report, 乬Breaking the Biological Barriers
to Cellulosic Ethanol: A Joint Research Agenda,乭
and a fact sheet on
the report may be viewed at 丂http://www.doegenomestolife.org/biofuels/.
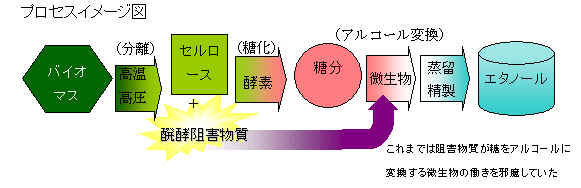
俼俬俿俤偲俫倧値倓倎丄僙儖儘乕僗宯僶僀僆儅僗偐傜偺僄僞僲乕儖惢憿怴媄弍傪嫟摨奐敪
丂嵿抍朄恖 抧媴娐嫬嶻嬈媄弍尋媶婡峔乮RITE乯偲Honda偺尋媶奐敪巕夛幮偱偁傞姅幃夛幮
杮揷媄弍尋媶強乮埲壓Honda乯偼丄怉暔桼棃偺嵞惗壜擻帒尮偱偁傞僜僼僩僶僀僆儅僗仸1偐傜僄僞僲乕儖傪惢憿偡傞媄弍偵娭偡傞嫟摨尋媶偺惉壥傪敪昞偟偨丅
丂婛懚偺媄弍偱偼丄庡偵僜僼僩僶僀僆儅僗偐傜僙儖儘乕僗椶傪暘棧偡傞岺掱偱暃師揑偵惗惉偝傟傞敭峺慾奞暔幙偑丄摐傪傾儖僐乕儖偵曄姺偡傞旝惗暔偺摥偒傪朩偘丄僄僞僲乕儖偺廂棪偑嬌傔偰掅偔側傞丅偙傟偑丄僜僼僩僶僀僆儅僗偐傜偺傾儖僐乕儖惢憿偺戝偒側忈奞偵側偭偰偍傝丄夝寛偡傞嶔偼崱傑偱尒弌偝傟偰偄側偐偭偨丅
丂崱夞丄RITE偺奐敪偟偨摐傪傾儖僐乕儖偵曄姺偡傞旝惗暔偱偁傞RITE嬠傪巊偄丄Honda偺僄儞僕僯傾儕儞僌媄弍傪妶梡偟丄敭峺慾奞暔幙偵傛傞埆塭嬁傪戝暆偵尭彮偝偣傞RITE-Honda僾儘僙僗偺奐敪偵惉岟丄廬棃偺僙儖儘乕僗宯僶僀僆僄僞僲乕儖惢憿僾儘僙僗偲斾妑偟偰傾儖僐乕儖曄姺偺岠棪傪旘桇揑偵岦忋偝偣傞偙偲偑壜擻偲側偭偨丅
| 嵿抍朄恖
抧媴娐嫬嶻嬈媄弍尋媶婡峔 乮Research Institute of Innovative Technology for the Earth丄捠徧RITE乯 |
||
| 奣梫 | 丂 | 抧媴娐嫬丄摿偵婥岓曄摦栤戣偵懳偡傞懳嶔媄弍偺婎慴揑尋媶傪峴偆尋媶婡娭偲偟偰丄擔杮惌晎偲柉娫婇嬈偺 嫟摨弌帒偵傛偭偰1990擭偵愝棫丅CO2偺挋棷媄弍傗戙懼僄僱儖僊乕尋媶側偳偵傛傞婥岓曄摦埨掕壔偵庢傝慻傫偱偄傞丅 |
| 強嵼抧 | 丂 | 嫗搒晎憡妝孲栘捗挰栘捗愳戜 |
| 棟帠挿 | 丂 | 廐嶳 婌媣 |
| 丂丂丂丂丂 | 丂丂 | 丂 |
| 姅幃夛幮 杮揷媄弍尋媶強丂婎慴媄弍尋媶僙儞僞乕 | ||
| 奣梫 | 丂 | Honda偺奐敪巕夛幮偱偁傞杮揷媄弍尋媶強偱丄婎慴媄弍暘栰偺尋媶奐敪傪扴摉偡傞婡娭丅1986擭4寧愝棫丅 擇懌曕峴儘儃僢僩偺ASIMO傗丄HondaJet偺奐敪偵壛偊丄僶僀僆暘栰傗僄僱儖僊乕暘栰偺婎慴尋媶傕庤偑偗偰偄傞丅 |
| 強嵼抧 | 丂 | 嶉嬍導榓岝巗 |
| 愑擟幰 | 丂 | 愳撶抭旻丂乮杮揷媄弍尋媶強 愱柋庢掲栶乯 |
丂
桝擖媊柋暷傪僶僀僆擱椏偵丂擾悈徣丄僄僞僲乕儖壔悇恑
丂擾椦悈嶻徣偼丄嵼屔偑愊傒忋偑偭偰偄傞惌晎偺嵟掅桝擖媊柋乮儈僯儅儉傾僋僙僗乯暷傪丄僈僜儕儞偺戙懼擱椏偲偟偰婜懸偝傟傞僶僀僆僄僞僲乕儖偺尨椏偲偟偰妶梡偡傞曽恓傪屌傔偨丅暷傗敒側偳偐傜僄僞僲乕儖傪惗嶻偡傞柉娫岺応偱丄尨椏偑懌傝側偔側偭偨応崌偵棙梡偡傞丅擭娫俀侽侽壄墌傪挻偊傞桝擖媊柋暷偺曐娗旓梡嶍尭偲偺堦愇擇捁傪慱偭偰偄傞偑丄攧媝壙奿偼攦偄擖傟壙奿傪壓夞傝丄懝幐偑弌傞偺偼妋幚偲傒傜傟傞丅
丂
丂嵟掅桝擖媊柋偵傕偲偯偔桝擖暷偺嵼屔偼丄崱擭俁寧枛帪揰偱俀侽俁枩僩儞乮尯暷姺嶼乯偵忋傝丄庡怘梡崙嶻暷偺擭娫廀梫偺係暘偺侾偵偁偨傞丅慡崙奺抧偺憅屔偱曐娗偡傞旓梡偼丄崱擭搙偼俀侾俈壄墌偵忋傞尒崬傒偩丅
丂惌晎偼俋俁擭偵僐儊帺桼壔傪庴偗擖傟丄崅娭惻傪壽偡戙傢傝偵堦掕検偺桝擖媊柋傪庴偗擖傟偨丅尰嵼偼暷崙丄崑廈丄拞崙丄僞僀側偳偐傜擭娫栺俈俈枩僩儞桝擖偟偰偄傞丅
擔杮宱嵪怴暦丂2006/11/16 丂丂丂丂
掗恖丄僶僀僆擱椏偵嶲擖丂墷廈偵惗嶻夛幮丂25%弌帒丂寉桘戙懼丄尰抧婇嬈偲慻傓
丂
惗嶻夛幮偼僶僀僆儊僞僲乕儖働儈儂乕儖僨傿儞僌(僆儔儞僟)偱丄掗恖偼俀俆%偵憡摉偡傞侾俆侽侽枩儐乕儘(栺俀俀壄俆愮枩墌)傪弌帒偟偨丅怴夛幮偵偼尰抧偱僶僀僆擱椏偺奐敪丒嫙媼傪庤妡偗傞僀乕僐儞僒乕儞(僆儔儞僟)偑栺俁俆%弌帒偟偨傎偐丄尰抧偺搳帒夛幮俀幮傕弌帒偟偨丅
奺幮偺僶僀僆擱椏傊偺庢傝慻傒
嶰堜暔嶻
丂丒僽儔僕儖崙塩愇桘夛幮儁僩儘僽儔僗偲摨崙偱偺惗嶻丒桝弌奼廩偵岦偗偨帠嬈壔挷嵏
丂丒儁僩儘僽儔僗丄僽儔僕儖揝峼愇戝庤儕僆僪僙偲摨崙偱偺僄僞僲乕儖暔棳岠棪壔偵岦偗帠嬈壔挷嵏
娵峠
丂丒07擭偐傜僒僢億儘價乕儖丄寧搰婡夿偲僞僀偱僒僩僂僉價傪尨椏偵僄僞僲乕儖惗嶻
丂丒07擭偐傜戝惉寶愝丄僒僢億儘價乕儖側偳偲嶄巗偱寶愝攑嵽傪尨椏偵僄僞僲乕儖惗嶻
埳摗拤彜帠
丂丒僽儔僕儖惌晎宯婇嬈側偳偲摨崙搶晹偱僶僀僆僄僞僲乕儖丄僶僀僆僨傿乕僛儖偺惗嶻岺応傪寶愝丄俀侽侾侽擭傔偳偵懳擔桝弌
僩儓僞帺摦幵
丂丒07擭弔偵僽儔僕儖偱僄僞僲乕儖偩偗偱憱傞乽僇儘乕儔乿搳擖
丂丒08擭偵傕杒暷偱崿崌斾85%傑偱懳墳偺彫宆僩儔僢僋敪攧傊
儂儞僟
丂丒僽儔僕儖偱崿崌斾20-100%懳墳偺乽僔價僢僋乿乽僼傿僢僩乿傪擭撪偵敪攧
丂丒堫傢傜傗宻側偳偐傜僄僞僲乕儖傪惢憿偡傞媄弍傪RITE偲嫟摨奐敪丅2-3擭撪偵検嶻媄弍傪妋棫
擔嶻帺摦幵
丂丒墷暷偱僄僞僲乕儖幵搳擖傪弨旛拞
僨儞僜乕
丂丒僄僞僲乕儖偵傛傞晠怘側偳傪杊偖晹昳偺奐敪嫮壔
怴擔杮愇桘
丂丒僩儓僞帺摦幵偲僶僀僆僨傿乕僛儖擱椏傪嫟摨奐敪
怴擱椏丄擔暷傾僋僙儖丂宱嶻徣丒嬈奅偑嶌嬈拝庤
丂娒棙宱嵪嶻嬈憡偼俀係擔丄擔杮帺摦幵岺嬈夛丄愇桘楢柨椉庱擼偲偺崸択夛傪奐偒丄僶僀僆擱椏側偳師悽戙帺摦幵擱椏偺晛媦偵岦偗偨姱柉嫟摨嶌嬈偵拝庤偟偨丅暷崙偱偼僽僢僔儏戝摑椞偑丄戙懼擱椏棙梡側偳偱僈僜儕儞徚旓傪崱屻侾侽擭娫偱俀妱尭傜偡怴曽恓傪昞柧丅妶敪壔偡傞擔暷偺愇桘戙懼僄僱儖僊乕惌嶔偺攚宨偵偼丄埨慡曐忈傗娐嫬懳嶔偺嫮壔偵壛偊丄帺摦幵嬈奅側偳偺愴棯傕偁傞
丂
擔杮宱嵪怴暦丂2007/4/18
僶僀僆擱椏丂捈愙崿崌偐壔崌暔棙梡
捈愙崿崌偱偼忲敪偱岝壔妛僗儌僢僌偺尨場暔幙偑憹偊丄悈暘偑崿擖偟僈僜儕儞偲暘棧偡傞偲帺摦幵晹昳偺晠怘偵偮側偑傞偲偺堄尒偑偁傞丅堦曽偱ETBE偼埨慡惈偺妋擣偑昁梫偲偺巜揈傕偁傞丅
奀奜偱偺僶僀僆僄僞僲乕儖偺棙梡
| 丂 | 崿崌棪 | 庡側尨椏 |
| 仴捈愙崿崌' | ||
| 暷崙 | 10%丄85% | 僩僂儌儘僐僔 |
| 僽儔僕儖 | 20-25%丄100% | 僒僩僂僉價 |
| 拞崙 | 10% | 僩僂儌儘僐僔丄彫敒側偳 |
| 僀儞僪 | 5% | 僒僩僂僉價 |
| ETBE(僄僞僲乕儖壔崌暔) | ||
| 僪僀僣 | 掅棪 | 儔僀敒丄彫敒 |
| 僗儁僀儞 | 3-7% | 彫敒丄戝敒 |
| 僼僼儞僗 | 6-7% | 彫敒丄僥儞僒僀 |
丂
丂
Platts 2008/5/16
Bill Gates investment vehicle slashes Pacific Ethanol stake
Microsoft founder Bill Gates has been selling off his stake in
beleaguered West Coast ethanol producer Pacific Ethanol, slashing
the shares held by his Cascade Investment company to 1.4 million from 10.5 million
over the last six months, according to securities filings.
High corn costs and planned new capacity is weighing down US ethanol industry stock prices.
---
May 06, 2008 CNN:
Gates beneficially owns, through his investment firm Cascade Investment LLC, 9.5 million shares, or an 18.5 percent stake based on 41.8 million shares outstanding as of April 23. According to a filing with the Securities and Exchange Commission, Cascade owns 7.5 million shares upon conversion of 3.75 million shares of Series A preferred stock and another 2 million shares directly.
Previously, Gates reported owning about 10.5 million shares, or a 21 percent stake in the Sacramento, Calif.-based ethanol producer.
ethanolproducer.com 2008/5/8
According to a filing May 5 with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission, Microsoft Corp. Chairman Bill Gates has reduced his holdings in Pacific Ethanol Inc. to 9.5 million, down from 10.5 million, out of 41.8 million shares outstanding. As a result, Gates乫 stake is reduced from 21 percent, or 10.5 million shares, to 18.5 percent in the Sacramento, Calif.-based corn ethanol producer and marketer.
Cascade owns 21 percent of Pacific Ethanol and has lost approximately $60 million on the stock since August. Cascade invested $84 million in the company in 2005.
According to a March SEC filing by Pacific Ethanol, 乬based on our current number of shares of common stock outstanding, Cascade Investment LLC has approximately 19 percent and Lyles United LLC has approximately 13 percent of all outstanding voting power as compared to approximately 8 percent of all outstanding voting power held in aggregate by our current executive officers and directors.乭
丂
Pacific Ethanol has ethanol plants in Madera, Calif.; Boardman, Ore.; and Burley, Idaho and has an additional plant under construction in Stockton, Calif.
丂
Pacific Ethanol was an up-and-coming pioneer in the West Coast biofuels movement when Gates, the co-founder of Microsoft Corp., agreed in November 2005 to buy $84 million worth of preferred stock. Shares in the company, then based in Fresno, jumped 10 percent on the news.
The past year has brought tough times. Profits have been depressed by a supply glut and the rising price of corn - the main ingredient in ethanol - and the company was staggered by millions in construction cost overruns. In March, Pacific Ethanol reported a $14.7 million fourth-quarter loss and was forced to sell $40 million in preferred shares to a contractor to ease a cash squeeze.
Nonetheless, the company has said it's still optimistic about ethanol's long-term outlook and is forging ahead with a plan to lock up the Western U.S. market. It recently opened its third wholly owned plant, in Idaho. A fourth plant, in Stockton, is under construction.
丂
----------
International
Herald Tribune 2007/11/19
Gates's investment fund to sell shares in ethanol producer
Cascade Investment, a company owned by Bill Gates, chairman of
Microsoft, is preparing to sell its shares in Pacific Ethanol,
which has lost almost two-thirds of its market value this year.
Cascade, which owns a 21 percent stake in the company, will
convert its preferred stock to 10.5 million common shares and
offer them to the public, according to a Pacific Ethanol filing
with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission. At the closing
price Friday, Gates has lost $24 million on the investment. He
paid $84 million for his stake in 2005.
Pacific Ethanol, based in Sacramento, California, has fallen 63
percent this year in Nasdaq composite trading, as the burgeoning 媫惉挿偡傞
supply of the fuel
additive drove prices down 25 percent. The company reported a
third-quarter loss last week of $4.8 million.
Pacific Ethanol produces about 80 million gallons, or 190 million
liters, of the additive annually at its plants in Madera,
California, and Boardman, Oregon. The company owns a 42 percent
stake in a 48 million-gallon plant in Windsor, Colorado.
There are 131 ethanol distilleries in the United States, with the
capacity to produce seven billion gallons of the fuel annually,
according to the Renewable Fuels Association in Washington.
Seventy-two plants under construction will almost double current
production.
POET of Sioux Falls, South Dakota, is the largest U.S. ethanol
producer. Archer Daniels Midland, based in Decatur, Illinois, is
the second biggest.
http://www.ethanolrfa.org/industry/locations/
Company 丂 Current Capacity
(mgy)Under Construction/
Expansions
(mgy)POET 丂 丂丂1,253 丂丂丂282 Archer Daniels Midland 丂 丂丂1,070 丂丂丂550 Pacific Ethanol Madera, CA 丂丂丂 40 丂 Boardman, OR 丂丂丂 40 丂 Burley, ID 丂丂丂 60 丂丂丂 Stockton, CA 丂 丂丂丂 50 (Total) 丂丂(140) 丂丂丂(50) Front Range Energy
(Pacific Ethanol偑42%曐桳乯Windsor, Colorado 丂丂丂 48 丂 April 29, 2008 丂Pacific Ethanol, Inc., the largest West Coast-based marketer and producer of ethanol, today announced start-up is complete at its Magic Valley production facility in Burley, Idaho.
The 60 million gallon per year Burley facility is located on 177 acres, with access to the Union Pacific Railroad, Eastern Idaho Railroad, and Interstate 84.
------
俶俤俢俷奀奜儗億乕僩 2008.2.20
彫婯柾僶僀僆儕僼傽僀僫儕乕丒僾儘僕僃僋僩偵DOE
偑彆惉乮暷崙乯
乗彜嬈婯柾偺1乛10 僒僀僘偺愝旛偵嵟戝1 壄1,400
枩僪儖乗
丂2008 擭1 寧丄暷崙僄僱儖僊乕徣(DOE)僒儈儏僄儖丒儃乕僪儅儞挿姱偼丄4
審偺彫婯柾僶僀僆儕僼傽僀僫儕乕丒僾儘僕僃僋僩偵丄4
擭娫(2007乣2010 梊嶼擭搙)偱嵟戝1 壄1,400
枩僪儖偺彆惉傪峴偆偙偲傪敪昞偟偨丅偙偺僾儘僕僃僋僩偼丄僐儘儔僪廈僐儅乕僗丒僔僥傿丄儈僘乕儕廈僙儞僩丒僕儑僙僼丄僆儗僑儞廈儃乕僪儅儞丄僂傿僗僐儞僔儞廈僂傿僗僐儞僔儞儔僺僢僘偱幚巤偝傟傞丅2012
擭傑偱偵僐僗僩嫞憟椡偺偁傞僙儖儘乕僗宯僄僞僲乕儖傪惢憿偡傞偲偄偆僽僢僔儏戝摑椞偺栚昗傪払惉偡傞偨傔丄彜嬈婯柾偺1乛10
僒僀僘偺僶僀僆儕僼傽僀僫儕乕偱條乆側尨椏傪巊梡偟偰怴婯曄姺媄弍傪僥僗僩偟丄彜嬈婯柾偺僶僀僆儕僼傽僀僫儕乕偺壱摦偵昁梫側僨乕僞傪庢傞丅彜嬈婯柾偺僶僀僆儕僼傽僀僫儕乕偼暯嬒偱堦擔700僩儞偺尨椏傪張棟偟丄擭娫栺2,000乣3,000
枩僈儘儞偺惗嶻検偱偁傞偨傔丄崱夞偺彫婯柾僾儔儞僩偱偼堦擔栺70
僩儞偺尨椏張棟偱擭娫250
枩僈儘儞偺惗嶻検傪尒崬傫偱偄傞丅
侾乯ICM 幮乮僇儞僓僗廈Colwich乯丄DOE
偺彆惉梊掕妟偼嵟戝3,000 枩僪儖
丂儈僘乕儕廈僙儞僩丒僕儑僙僼偵寶愝梊掕偱偁傝丄擾嬈巆熢暔乮僩僂儌儘僐僔偺慇堐傗宻梩丄僗僀僢僠僌儔僗丄僜儖僈儉側偳乯傪娷傓懡條偱崱擔揑偵堄枴偺偁傞尨椏傪巊梡偡傞梊掕偱偁傞丅
俀乯Lignol Innovations
幮乮儁儞僔儖儀僯傾廈僶乕僂傿儞乯丄DOE
偺彆惉梊掕妟偼嵟戝3,000 枩僪儖
丂僐儘儔僪廈僐儅乕僗丒僔僥傿偺愇桘偺惛惢岺応偲摨偠晘抧撪偵暪愝梊掕偱偁傝丄乽biochem-organisolve乮僶僀僆壔妛丒桳婡梟嵻乯乿偲屇偽傟傞梟嵻傪巊梡偟偰丄峝栘傗擃栘偺攑嵽傪僄僞僲乕儖傗巗斕惢昳偵曄姺偡傞梊掕偱偁傞丅
俁乯Pacific Ethanol
幮乮僇儕僼僅儖僯傾廈僒僋儔儊儞僩乯丗DOE
偺彆惉梊掕妟偼嵟戝2,430枩僪儖
丂僆儗僑儞廈儃乕僪儅儞偵寶愝梊掕偱偁傝丄BioGasol
幮偑撈帺奐敪偟偨曄姺僾儘僙僗傪梡偄偰擾嬈巆熢暔偲怷椦巆熢暔傪僄僞僲乕儖偵曄姺偡傞丅Pacific
Ethanol幮偼暷崙惣晹偱傕桳悢偺嵞惗壜擻側掅扽慺擱椏偺惢憿嬈幰偱偁傞丅僇儕僼僅儖僯傾廈僒僋儔儊儞僩偵杮幮傪峔偊傞摨幮偼丄僆儗僑儞廈偵偁傞帺幮偺僩僂儌儘僐僔桼棃僄僞僲乕儖曄姺巤愝偵僙儖儘乕僗宯僄僞僲乕儖偺曄姺擻椡傪憹愝偡傞偙偲傪寁夋偟偰偄傞丅
係乯Stora Enso North America
幮乮僂傿僗僐儞僔儞廈僂傿僗僐儞僔儞儔僺僢僘乯丄DOE偺彆惉梊掕妟偼嵟戝3,000
枩僪儖
丂僂傿僗僐儞僔儞廈僂傿僗僐儞僔儞儔僺僢僘偵寶愝梊掕偱偁傝丄怷椦攑婞暔傪梡偄偰僼傿僢僔儍乕丒僩儘僾僔儏朄
偵傛傞僨傿乕僛儖擱椏傊偺曄姺偑寁夋偝傟偰偄傞丅