 Marl
Marl
| frequently asked
question Are you
really changing the name of British Petroleum to Beyond Petroleum ? |
(Associated Press, April
13, 2000)
History: BP's predecessors include Burmah Oil and Anglo-Persian
Oil. Anglo had the first oil strike in the Middle East in 1908;
the British government bought 51 percent in 1914, eventually
selling its interest in 1987. Anglo's Iranian operations were
seized in 1951, but returned by the Shah in 1953. Changed name to
BP in 1954. Had North Sea oil strikes in 1970. Prudhoe Bay,
Alaska oil discovered in 1969; BP traded its Alaska interests for
55 percent of SOHIO in 1970; as SOHIO it used Alaskan profits to
buy Kennecott. In the 1980s BP bought Purina Mills and the rest
of SOHIO. Kuwait owns 10 percent (down from 22 percent) of BP. BP
had 1990 sales of $59 billion on oil and gas interests in 20
countries. BP also sells chemicals (see BP Chemicals) (Hoover's
Handbook of World Business 1992, p. 164). Owns British Gas (Whole
World Oil Directory 1991).
British
Petroleum completed its $55 billion acquisition of Amoco on Dec.
31, 1998, creating
Britain's biggest company and the third largest oil company in
the world. The new company will be called BP Amoco Plc. The deal
cleared its final hurdle Wednesday when the U.S. Federal Trade
Commission approved the deal on condition that the merged
companies sell 134 gasoline stations and nine terminals storing
oil products (Reuters, Jan. 1, 1999).
In April 2000, the U.S. Federal Trade Commission
"unanimously approved BP Amoco PLC's $27.6 billion purchase of
Atlantic Richfield Co. after the company agreed to sell Arco's
Alaskan large oil holdings. The merger, approved by the
commission in a 5-0 vote, will create one of the world' largest
oil companies. The company said it would move swiftly to conclude
the acquisition. The approval requires BP Amoco to sell all of
Arco's oil holdings in Alaska within 30 days to resolve
anticompetitive problems. The FTC had opposed the merger because
of concern that the combination, without such divestitures, would
dominate the West Coast oil market. BP Amoco already has agreed
tentatively to sell the holdings to Phillips Petroleum Co... The
merger creates the second largest nongovernment oil company in
world behind Exxon Mobil Corp., a merger that received FTC
approval last November."
Supplying polyethylene to the world
The BP Polyethylene Business is a leading producer of polyethylene, with a full range of low density polyethylene (LDPE), linear low density polyethylene (LLDPE) and high density polyethylene (HDPE) products for the packaging, agricultural, consumer goods and construction sectors. We are also major licensors of cutting edge process and catalyst technologies to the global polyethylene market.
The Polyethylene Business is one of the largest business units in BP's Chemicals stream, with access to over 1.9 million tonnes per annum of polyethylene capacity.
Innovex LLDPE film productsThe business supplies the film market sectors with Innovex linear low density resins based on both butene (C4) and higher alpha olefin (C6) comonomers.
Novex LDPE film and coating products
Novex low density resins include a comprehensive range of homopolymer and copolymer grades, additive packages and natural masterbatches.
Innovene Advanced gas phase technology
The Innovene gas phase manufacturing process has been licensed worldwide, and almost 40 licensees currently use this ground-breaking technology.
Rigidex HDPE Moulding Products
Rigidex HDPE is used many sectors of the packaging industry, with products for applications as diverse as small bottles, large drums and tanks, crates, pails, bottle caps, toys, technical parts and fibres.
Rigidex Pipe products
Rigidex HDPE and MDPE products supply the utility services and distribution industries. The main applications are in pressure and non-pressure piping systems, the coating of steel pipes with polyethylene, and the production of ducting to carry cables.
Wire & Cable Resins and compounds
Resins and compounds based on LDPE, LLDPE and HDPE, manufactured mainly at Cologne, Germany are supplied to the wire and cable market.
Strength in Depth - global reach
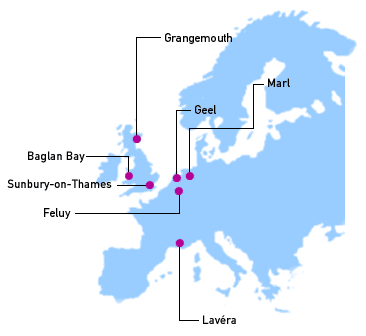
Our plants based at Grangemouth in Scotland, Lavera in France, and Cologne in Germany produce high density and linear low density polyethylene for the film, coating, moulding, pipe, masterbatch and wire and cable markets. BP has three joint ventures producing polyethylene in the Asia Pacific region; PT Peni in Indonesia; PEMSB in Malaysia and Bataan Polyethylene Corporation in the Philippines.
BP Amoco
BP Amoco produces olefins at two
manufacturing sites in Europe, Grangemouth in Scotland and Lavera in France. The sites have a combined
ethylene cracking capacity of approximately 1.3 million tonnes
per annum. Olefins produced at these two sites are used to supply
BP Amoco derivatives, along with various external customers and
joint venture partners in Europe and East Asia.
Two former Amoco sites located at Feluy and Geel in Belgium have recently been integrated
into the business. Feluy is a net consumer of 315,000 tonnes of
ethylene per annum, whilst Geel consumes 480,000 tonnes of
propylene. The Baglan Bay plant in Wales is also a consumer of
ethylene and propylene for the production of isopropanol, ethanol
and vinyl acetate monomer.
Our European sales office,
located at Sunbury-on-Thames near Heathrow, services the UK,
France, Germany and Benelux. The BP Amoco Olefins European
headquarters is also located in Sunbury-on-Thames.
At the heart of the Grangemouth site are two crackers. These produce feed materials used by derivatives including the PP3 (polypropylene), PEX, Innovex and Rigidex (polyethylene) plants. These plants produce various grades of low and high-density polyethylene used in the manufacture of thousands of everyday items ranging from stretch wrap and fruit bags to gas pipes and plastic bottles. Raw materials for both crackers come directly from the North Sea's Forties pipeline system.
The Grangemouth Unit 4 (G4) can crack 250,000 tonnes of ethylene per annum from both gas and light distillate feedstocks. The Kinneil Grangemouth (KG) unit is a gas cracker using mainly propane and butane as its raw materials. It has a capacity of 450,000 tonnes of ethylene per year. An effluent treatment plant that treats wastewater from both KG and G4 is one of KG's key features. This has radically improved effluent quality and is a testament to BP Amoco's commitment to environmental improvement. Any further waste products from both plants are ultimately recycled or used as fuel. Nothing is wasted.
The two units produce 700KTe of ethylene per annum between them, although this capacity will increase to more than 1,000KTe per annum by 2001.
Olefins at Lavéra are manufactured indirectly by BP Amoco through Naphtachimie, a 50:50 joint venture with Elf Atochem. Naphtachimie's Cracker 4 produces 700,000 tonnes ethylene, 500,000 tonnes propylene and 120,000 tonnes of Butadiene per annum. BP Amoco uses 50% of this output to supply derivative plants such as Appryl (Polypropylene) and Oxochimie (Oxo-alchohols) and third party customers.
The BP Amoco Chemicals Feluy plant, located just south of Brussels in Belgium, is the largest western European producer of linear alpha olefins (LAOs) and the largest European producer of polyalphaolefins (PAOs). To meet the requirements of the industry, production capacity of LAOs is now 300,000 tonnes per annum. PAO production capacity on the site is 55,000 tonnes.
BP Amoco Chemicals facility in Geel, Belgium is located on a 115 hectare site, 45 km east of Antwerp.
The plant's operations can be divided into two main streams. The commodity and speciality stream manufactures 900,000 tonnes of purified terephthalic acid (PTA) and 130,000 tonnes of purified isophthalic acid (PIA) per annum. These are used in polyester fibres, films and packaging resins, as well as in coatings and glass reinforced plastic resins. A 450,000 ton paraxylene plant on the site provides the raw material for the PTA. The polymer stream manufactures 500,000 tonnes per annum of polypropylene resins for use in fabrics, fibres and moulded plastics, for which the site consumes 480,000 tonnes of propylene per annum.
BP Amoco Chemicals Marl in Germany consumes 100,000 tonnes of ethylene and 300,000 tonnes of benzene per annum. The plant manufactures styrene, polystyrene (PS) and expandable polystyrene (EPS). The acquisition of the Marl facility in 1997 has made BP Amoco Chemicals the second largest supplier of PS and EPS in Europe.
BP Amoco Chemicals Baglan Bay plant is located in Port Talbot, 13 kilometers east of Swansea on the south coast of Wales. It is one of the company's three major petrochemical production centres in the UK. The 1000 acre site manufactures ethanol, vinyl acetate monomer (VAM) and isopropanol (IPA) from ethylene and propylene feedstock.
BP Amoco's Olefins business in
Asia is run from three offices based at Kuala Lumpur in Malaysia,
Jakarta in Indonesia and Singapore.
The strategic function of BP Amoco Olefins operations in Asia is
to source and supply competitively advantaged olefins to our
Joint Venture polymer manufacturing assets in the Asia Pacific
region. We supply approximately 140,000 tonnes of ethylene to our
joint venture polyethylene plants in Merak, Indonesia and Bataan,
Philippines. A further 250,000 tonnes of propylene are supplied
to our joint venture site at Balongan, Indonesia and to other
third party customers.
Ethylene
BP Amoco has a 51% share in the PT Petrokimia Nusantara Interindo (PT PENI) polyethylene plant in Merak, Indonesia. Other joint venture partners include PT Arseto Petrokimia (24%), Mitsui and Co Ltd (12.5%) and Sumitomo Corporation (12.5%).
*PT Peni for sale: BP
The plant manufactures 450,000 tonnes per annum of Linear Low Density Polyethylene (LLDPE), and High Density Polyethylene (HDPE) using BP Amoco's Innovene technology.
In the Philippines, BP Amoco owns a 38% share in the Bataan Polyethylene Corporation (BPC) plant at Bataan. Other joint venture partners include Petronas and Sumitomo Corporation. Plant capacity will be 250,000 tonnes per annum of LLDPE and HDPE when operations commence in mid 2000.
*Bataan PE for sale: BP
BP Amoco also has a 60% share in Polyethylene Malaysia (PEMSB) and a 15% share in Ethylene Malaysia (EMSB) at Kertih.
BP Amoco has a 10% share of PT Polytama Propindo (PTPP) polypropylene in Balongan. The
plant produces 180,000 tonnes per annum of polypropylene, based
on Himont technology.
The Olefins Asia business is responsible for marketing all
propylene (approximately 210,000 tonnes per annum) produced at
the Pertamina
refinery at Balongan in Indonesia. Olefins Asia also manages the propylene
pipeline supply operation between the refinery and the Polytama
site.
*Polytama Propindo was established as a joint venture between Tirtamas Majutama with 80% stake, BP Chemicals owns 10% share and Japan’s Nissho Iwai owns the rest 10%.
Tirtamas Majutama had agreed to hand over its assets in the multibillion dollar project to Indonesian Bank Restructuring Agency(IBRA).
BP Solvay Polyethylene North America
(Solvay holds a 51 percent stake and BP owns the remainder.)
BP Solvay Polyethylene North
America is one of the global marketplace's most exciting new
companies. A joint venture between British Petroleum (BP) and
Solvay S.A., our combined roots in the chemical business go back
almost 140 years.
Annually BP Solvay Polyethylene produces 1.8 billion pounds of
Fortiflex high-density polyethylene (HDPE) at its production facilities in Deer Park,
TX. Most of the HDPE produced is in the form of plastic pellets,
shipped in railroad hopper cars and bulk trucks..
Fortiflexョ HDPE resins are
used extensively in a wide range of consumer and industrial
products manufactured by many different processes.
At BP Solvay Polyethylene North America, we take product quality
and customer satisfaction very seriously. We have the toughest
standards in the industry and we back them up with our
No-Nonsense Pledge . We make sure our customers have the products
they need, when and where they need them.
(2001/11/1 release) http://www.bpsolvaype.com/Press.html#21
Solvay's agreement with BP enters into force
BP completes deal to strengthen core polymers businesses
Solvay’s agreement with BP enters into force
・Strengthening of Solvay’s position in high-margin Specialty Polymers
・Birth of "BP SOLVAY POLYETHYLENE" joint venturesFollowing the regulatory clearance received by the United States Federal Trade Commission (FTC) in July, Solvay has just received the final go-ahead from the different national authorities and from the European Commission on the transaction signed with BP in August 2001. The competition authorities required no modification of the agreement.
Being effective as from November 1, 2001, with retroactive effects as from October 1, 2001, the three-way agreement includes:
- The acquisition by Solvay of BP’s engineering polymers business. It will increase significantly Solvay’s sales in high performance engineering polymers and performance compounds. Total turnover in this fast-growing market will reach approximately EUR 900 million (33% of the plastics sector) and will grant Solvay a global leadership position in the high performance plastics industry.
The entire activities will be managed by Vincenzo Morici, Manager of Solvay's Specialty Polymers and Performance compounds. The transaction considerably expands Solvay’s geographic presence in Specialty Polymers and the range of products that it can offer to a wider variety of industries.
- The setting up of two joint ventures in high density polyethylene ("HDPE"), which together are one of the leading players worldwide, with a total turnover of approx. EUR 2.0 billion.
Joint ventures in Europe (50/50) and in the USA (51/49) have been created under the new name "BP Solvay polyethylene". European activities will be managed by Robin McGill (formerly with BP) and US activities will be managed by Foster Brown (formerly with Solvay). The new global force in the manufacture, sales and marketing of HDPE will offer the customers the widest range of HDPE products and services worldwide.
- And the divestment of Solvay’s Polypropylene (PP) activities where it was not amongst the global leaders (ranked 12th with annual sales of EUR 500 million).
Besides the transfer of assets, the deal generates for Solvay a/o. an up front cash payment of EUR 80 million from BP and strengthens the HDPE business through security of ethylene supply. The joint venture agreements also define the conditions of exercise of puts and calls between both parties over their interests in the joint ventures.
"Through this agreement, Solvay is well placed to respond to the challenges of competitiveness, leadership and growth of the twenty-first century by combining the best from the strengths and traditions of the two partners" said Alois Michielsen, Chief Executive Officer. "With increased position in high-margin Specialty Polymers and strong leading position in HDPE, the Group reduces its exposure to petrochemical cycle while increasing the value of its product portfolio".
Solvay is an international chemicals and pharmaceuticals group with headquarters in Brussels. It employs about 32,000 people in 50 countries. In 2000 its consolidated sales amounted to EUR 8.9 billion generated by its four activity sectors: Pharmaceuticals, Chemicals, Plastics and Processing. Solvay is listed in the Euronext 100 index of top European companies. Details are available at www.solvay.com.
BP completes deal to strengthen core polymers businesses
BP has completed its deal with Solvay, announced in December 2000, significantly strengthening its core polyolefins businesses in Europe and the USA.
As result of the deal, BP has added Solvay’s global polypropylene business to its existing business and the two companies have combined their high-density polyethylene (HDPE) businesses into two joint ventures. BP has also transferred its non-core engineering polymers business to Solvay.
Completion of the deal followed approval from the European Commission and other regulatory authorities.
The deal makes BP the world’s second largest producer of polypropylene. The two HDPE joint ventures ? BP Solvay Polyethylene Europe (50 per cent BP, 50 per cent Solvay), led by Robin McGill from BP, and BP Solvay Polyethylene North America (49 per cent BP, 51 per cent Solvay), led by Foster Brown from Solvay ? will together also be a leading player in their sector.
"This is a significant step in repositioning and upgrading our chemicals portfolio," said Byron Grote, chief executive of BP’s chemicals businesses. "The deal expands BP’s worldwide reach in our core petrochemicals businesses, while exiting a non-core business."
He added: "Our priority will now be to fully integrate the polypropylene businesses and operate the HDPE partnership to access maximum synergies from these combinations."
2003/7/9 Dow Jones Business News
Solvay, BP JV Restructures US Production Facilities
Belgian chemical and pharmaceuticals company Solvay SA (B.SOL) Wednesday said that its U.S. joint venture with BP PLC - BP Solvay Polyethylene North America - will discontinue production of 260 million pounds of high density polyethylene (HDPE) capacity from three small-capacity lines at its Deer Park, Texas manufacturing site at the end of July. The capacity being removed from the Deer Park site is being replaced by production from a new 700 million pound HDPE slurry loop plant at Cedar Bayou, Texas, in which BP Solvay Polyethylene owns a 50% interest.
The recent, successful startup of the new Cedar Bayou, Texas HDPE plant, jointly owned by BP Solvay Polyethylene North America and Chevron Phillips Chemical Company L.P, enables BP Solvay Polyethylene to improve the overall economics and efficiency of its operations.
"This move, previously publicized in November 2001, strategically places our company in the position to continue providing the level of preferred service to our customers we have established at BP Solvay Polyethylene North America. At the same time we will be operating from a more efficient manufacturing base," said Gary Miertschin, Commercial Vice President of the joint venture.
BP Solvay Polyethylene North America is a joint venture between subsidiaries of BP and Solvay America, Inc. It combines the worldwide strengths of two industrial leaders to form a powerful global presence in the HDPE industry. The joint venture when combined with its European affiliate together constitute the third largest HDPE producer in the world, with a total of six production sites in Europe and the United States, and a total annual capacity of 4.6 billion pounds.
2000/12/19 Solvay
Major activity exchange between Solvay and BP
SOLVAY announced that it signed with BP a Memorandum of Understanding aimed at strengthening its portfolio. The agreement would lead to SOLVAY's transfer of its polypropylene (PP) business to BP and to BP's transfer of its engineering polymers business to SOLVAY. SOLVAY would also form joint ventures with BP in high density polyethylene (HDPE) in Europe and the Americas. The future of these joint ventures has been agreed upon by both parties (global turnover of approx. EUR 2.0 billion).
In Europe, the two companies would combine their European high-density polyethylene (HDPE) businesses into a 50-50 joint venture.
In the US, the agreement would lead to SOLVAY and BP creating a 51-49 joint venture for SOLVAY's current HDPE business.
"This envisaged transaction would represent a further step in the ongoing repositioning of SOLVAY businesses, especially in Plastics", said SOLVAY CEO, Mr. A. Michielsen. 'It clearly illustrates SOLVAY's strategy of developing leadership positions, while moving into growing, innovative, high-yield markets, such as engineering polymers. This transaction would boost our growth and reduce our cyclicality and diversification".
"With a turnover of about EUR 700 million in engineering polymers, SOLVAY would take a leading global position in the high-growth high performance engineering polymers industry offering a broad range of competitive products", Alois Michielsen continued.
"Because of ongoing consolidation in the sector, our PP operations (turnover of about EUR 500 million) have more difficulties to compete effectively in that market. Exiting this business would contribute to focus on our existing global competitive leaderships", he concluded.
This Memorandum has been approved by SOLVAY and BP Board of Directors. The proposed transaction is subject to due diligence, to regulatory approval by the relevant authorities, as well as consultation with workers' representatives. Completion is anticipated in June 2001.
Further communication on this important deal will follow during the second quarter 2001 together with disclosure of financial details agreed upon by both parties.
SOLVAY is an international pharmaceutical and chemical group with headquarters in Brussels. It employs about 33,000 people in 50 countries. In 1999 its consolidated sales amounted to ?7.9 billion generated by its four activity sectors: Chemicals, Plastics, Processing and Pharmaceuticals. SOLVAY is listed in the Euronext 100 index of top European companies
Notes to editors:
High performance and engineering polymers.
SOLVAY's existing high performance and engineering polymers business involves 7 production units that are located in Tavaux (France), Rheinberg (Germany), Oudenaarde (Belgium), Roccabianca (Italy), Grand Prairie, Texas, Mansfield, Texas, and Decatur, Alabama. Ranges of products includes copolymers made from polyvinylidene chloride (IxanR), a wide variety of polyvinylidene fluoride grades (SolefR), reinforced polyarylamide-based compounds (IxefR) and polyphenylene sulfide (PrimefR) compounds, polypropylene elastomer compounds (SequelR) and crosslinked polyethylene compounds (PolydanR).
BP's engineering polymers business includes its world-class line of thermoplastics and specialty polymers, known by the brand names of UdelR, RadelR, AmodelR, XydarR, TorlonR, and KadelR. The polymers are characterized by high-temperature resistance and have applications in the automotive, aerospace, industrial, medical and electronics industries, among others. To be included in the engineering polymers transaction are manufacturing plants in Atlanta, Georgia; Augusta, Georgia; Marietta, Ohio; and Greenville South Carolina, and the business's headquarters and research & development center in Alpharetta, Georgia. Also included in the transaction are technical and marketing operations located in North America, Europe, Southeast Asia, and Japan.
After this transaction, SOLVAY will offer a range of high performance and engineering polymers with sales of about EUR 700 million in 2000, produced at 11 sites in Europe and the US. In most market segments, SOLVAY will be able to provide customers a better geographic reach, an improved technical service and a larger choice of products and solutions.
Polypropylene business
BP is the world's third largest producer of polypropylene (including its share to come from the dissolution of its Appryl joint venture with Atofina, and the equity share of the ARCO PP joint venture with Itochu in California) with production totaling almost 2.3 million tons per year from sites in the Grangemouth, Scotland (270 kta); Lavera, France (140kta); Geel, Belgium (500kta); Chocolate Bayou, Texas (900Kta) Cedar Bayou, Texas (300kta) and Carson, California (165 Kta).
SOLVAY is currently the world's twelfth largest polypropylene producer, with production at three sites: Lillo, Belgium (130kta); Sarralbe, France (270kta); and Deer Park, Texas (380kta).
After this transaction, BP would operate 3.1 million tons/year of polypropylene production at 9 sites.
High-Density polyethylene business
SOLVAY produces a total of around 1.5 million tonnes of HDPE per year, making it the world's fifth largest producer of the polymer. It produces HDPE at five sites around the world: Lillo, Belgium (165kta); Sarralbe, France (165kta); Rosignano, Italy (190kta); Deer Park, Texas (880kta) and Santo Andre, Brazil (70kta).
In Europe, BP produces HDPE at Grangemouth, Scotland (290kta with another 185kta onstream in February 2001) and Lavera, France (225kta). BP's existing joint venture HDPE production in Indonesia, Malaysia and the Philippines will not be contributed to the joint ventures. BP will continue to operate its own low and linear low density polyethylene business. This comprises LLDPE at Grangemouth Scotland (300kta), LDPE at Wilton, England (90kta) and a LDPE plant (350kta) and a LLDPE plant (220kta) contained within the Erdoelchemie joint venture (50/50 with Bayer).
After this transaction, the HDPE joint ventures would have a total capacity of 2.2 million tons/year with 7 production sites.
(BP 18 April 2000 )
BP Amoco combination with ARCO expands BP Amoco's Polypropylene capacity
BP Amoco announced today that, as a result of its combination with ARCO, the company will assume two thirds ownership in ARCO Polypropylene, LLC, a joint venture between ARCO and the Itochu Corporation of Japan.
The joint venture consists of a recently constructed 200,000 tonne per year polypropylene plant in Carson, California. The plant started producing polypropylene in December 1999. The joint venture's initial focus is the West Coast and export customers.
"We look forward to assuming our position as majority shareholder in ARCO Polypropylene, LLC, and to working with our partner in the venture to determine how to maximise synergies among ARCO Polypropylene, LLC and BP Amoco's leading worldwide polypropylene position," said Mike Graff, BP Amoco polypropylene business unit leader.
Polypropylene is used in a wide array of products such as appliances, automotive parts, carpeting and packaging. BP Amoco is one of the world's largest polypropylene producers with 2,000,000 tonnes per year of capacity.
Amoco is a world-wide producer and marketer of oil, natural gas, petroleum products, chemicals and solar power. The London-based company had 1999 revenues of approximately US $100 billion.
→ 伊藤忠15%に
→ BP
100%に (伊藤忠はアジア、南米のSales agent)
BP says it will permanently close about 32% of its North American polypropylene (PP) capacity. The company will shutter two unitsーa 261,000-m.t./year plant at Bayport, TX and a 205,000-m.t./year unit at Chocolate Bayou, TX. BP idled the Chocolate Bayou unit late last year, citing weak demand and poor margins. The Bayport plant will be closed by June. Employees affected by that shutdown will be redeployed to other positions at its south Houston refining and petrochemical complex, says BP.
The closures will leave the company with PP capacity of 625,000 m.t./year at Chocolate Bayou, and 386,000 m.t./year at Deer Park, TX. BP obtained the Deer Park plant as part of a swap deal with Solvay Polymers. BP also has about 180,000 m.t./year of PP production at a joint venture with Itochu at Carson, CA, obtained in its 2000 acquisition of Atlantic Richfield.
Weak market conditions and oversupply have prompted several PP producers to rationalize capacity. Basell idled its PP plant at Bayport, TX in late 2000 as part of a 10% shutdown in its worldwide PP capacity (CW, Jan. 3, 2001, p. 15); Huntsman closed about 27,000 m.t./year of capacity at Odessa, TX in January. PP prices recently recovered, following a year of declines; producers pushed through a 5-cts/lb increase.
Formosa Plastics recently brought onstream almost 160,000 m.t./year of new PP capacity at Point Comfort, TX (CW, March 6, p. 37). Phillips Petroleum is expected to start up a 350,000-m.t./year PP plant at Linden, NJ by the end of June.
Platts 2002/10/25
Indonesian PE joint venture PT Peni for sale: BP
Indonesian polyethylene joint venture PT Peni is to be sold after
shareholders (BP 75%, Mitsui Corp 12.5% and Sumitomo Corp 12.5%)
decided that the verticle integration needed to improve the JV's
profitability would be best achieved under new leadership, a BP
spokesperson said Friday.
"All shareholders have agreed that this move is in the best
interest of the company," said the source adding that no
deadline had been put on sale discussions which had already
started. Both local and foreign ethylene suppliers were
understood to be interested at this stage but no decision had
been taken on the future ownership. The joint venture was
established in 1993, and manages a 450,000mt/yr high
density/linear low swing PE plant at Merak.
PT Peni had previously considered a JV with local ethylene and PE
major, Chandra Asri but the timing had not been suitable,
according to BP. The spokesperson said, "the shareholders
have now decided that we do not have the time or resources to
commit to a merger in order to secure ethylene supply [for this
unit]."
BP had also
agreed in-principle to sell its 39% share in a PE JV in the
Philippines, Bataan Polyethylene, because of poor returns. Bataan's two PE
plants have been idle for more than one year. They had come
online in 2000 and have a combined capacity of 250,000 mt/yr.
The plants had not been cost competitive either because the
Philippines does not produce ethylene locally. BP also operates a
PTA joint venture in Indonesia but has no intentions to sell its
stake, the source confirmed.
BP Planning New
World-Scale PTA Plant In Belgium
BP announced today that it has begun detailed engineering design
for the construction of a new world-scale purified terephthalic
acid (PTA) production plant at its Geel petrochemicals site in
Belgium.
The detailed design for the new plant will be carried out by
Technip Italy (the engineering centre for the Technip-Coflexip
Group) over the next nine months. Subject to final BP and other
approvals, the company anticipates construction on the new plant
would begin in 2004 with the plant coming on stream in early
2006.
The plans envisage construction of a 700,000 tonnes a year PTA
plant at Geel. Output from the plant will be primarily targeted
at the European market, particularly at fast-growing European
polyethylene terephthalate (PET) production, for which PTA is a
core feedstock.
Iain Conn, chief executive, BP petrochemicals, said: "PTA is
one of BP's core strategic petrochemical products and this
investment will reinforce our global leadership position in the
business."
Mike Buzzacott, group vice president, BP petrochemicals, added:
"This new plant will use our latest generation technology
and be extremely well placed to meet the growing demand for PTA
across Europe. It also underlines the importance of the Geel site
to BP, building on the first-class people, experience and
infrastructure available there."
The new plant will confirm Geel as one of BP's main petrochemical
manufacturing sites worldwide. The new PTA unit will bring Geel's
total PTA production capacity to approximately 1.7 million tonnes
a year. In addition to PTA, the Geel site also produces
approximately 420,000 tonnes a year of paraxylene, the feedstock
for PTA production, 120,000 tonnes a year of purified isophthalic
acid (PIA), and 480,000 tonnes a year of polypropylene.
BP is a world
leader in the production of PTA, with worldwide production
capacity of some 6 million tonnes a year. In addition to European
PTA production at Geel, BP also produces PTA from plants in the
USA, Brazil, Korea, Indonesia, Malaysia and Taiwan. BP's latest PTA
production site, the 350,000 tonnes a year
Zhuhai (珠海) joint venture in southern China, was
successfully commissioned in January 2003. (BP Zhuhai Chemical Company Limited)
BP is one of the world's largest oil, gas and petrochemicals
companies with 2002 chemical sales of $13 billion and production
of some 27 million tonnes.
Asian Oil &
Gas 2000/11/1
中国JV完成
PTA to the
fore in BP ventures
The official groundbreaking for a world-scale purified
terephthalic acid (PTA) plant took place in Zhuhai, one of
China's special economic zones, in November. Targeted for
completion in December 2002, the $408 million complex will be
owned and operated by the Amoco Zhuhai Chemical Company, a three-year-old joint
venture between BP (80%), the Fuhua Group, a subsidiary
of the Port Enterprise Group (15%) and the China National
Chemical Fibre Company (5%).
Zhuhai is situated in south China's fast-developing coastal
province of Guangdong, which has attracted 60% of the total $2.5
billion project investment already made by BP, Amoco and Arco in
China since they started developing business there in the 1970s.
PTA is the primary and preferred raw material for making
polyester fibres, films and container resin. 'The PTA market in
China is very strong, growing faster than any other part of the
world at 8% a year,' Zhuhai general manager Linda Shum tells the
October edition of BP house magazine Horizon. 'In fact, it's the
only country in the world that has a PTA deficit. Demand is near
4 million tonnes a year yet production capacity is only 2 million
tonnes. China has to import the balance.'
The new plant will have a nominal capacity of 350,000 tonnes a
year which, according to Shum, 'can be easily expanded once any
initial teething problems are ironed out'.
A PTA alliance is also being forged at a national level in China.
BP announced in September that it intended to invest up to $400
million in the Sinopec initial public offering. Separately, and
among a variety of initiatives spanning the oil and gas sector,
the two companies signed a memorandum of understanding to build a
world-scale PTA manufacturing facility.
This plant will be integrated into the Caojing (formerly Jinshan)
ethylene project being undertaken by another joint venture
between BP and Sinopec, the Shanghai Petrochemical Company.
http://www.taiwanheadlines.gov.tw/20020730/20020730b6.html
July 30, 2002
China American Petrochemical to become top PTA producer
China American Petrochemical Co. (CAPCO) will become the world's
top supplier of pure terephthalic acid (PTA) after its sixth PTA
plant starts production in early 2003.
CAPCO, capitalized at NT$7.07 billion (US$211 million), already
has five PTA plants in Taiwan. The sixth plant will boost its
output capacity to over 2 million metric tons per year.
The new plant is located in an area adjacent to Taichung Harbor.
The district had been reserved for the Bayer Group of Germany for
the manufacturing of TDI. But Bayer scrapped the plan due to
strong local opposition.
Lee Tang-moh, senior vice president of CAPCO, said the sixth PTA
plant is designed to meet the needs of the textile companies
located on the east coast of mainland China following the three
direct links in trade, transportation, and postal services
between the mainland and Taiwan.
But the new plant will also cater to demand from the U.S. and
European markets, Lee added. CAPCO is a joint venture of BP-AMOCO,
which has a 50 percent stake, and Taiwan's state-run Chinese
Petroleum Corp., which holds 25 percent.
21 August 2001
BP to close Wilton polyethylene plant
BP announced
today that it will close its low density polyethylene (LDPE)
manufacturing operations at Wilton on Teesside. The company cited
difficult market conditions as the reason for closing the 100,000
tonne a year plant.
"It is with deep regret that, despite the efforts of
everyone at the site and the number of changes embraced in recent
years, we have had to make today's announcement," said
Donald Austin, BP Wilton site manager.
"In a highly competitive market, it has been increasingly
difficult to maintain profitability at the plant. The plant's age
and related high costs of production and maintenance combined
with competition from newer, larger plants have made Wilton
unprofitable and led to this decision."
The plant will cease production at the beginning of October.
Decommissioning is expected to continue until the end of the
year, and the plant will be dismantled and land cleared during
2002.
Consultations will take place immediately with the 81 BP
employees who work at the plant regarding their future and BP
commits to ensuring that every effort is made to relocate those
with the appropriate skills to other BP locations, or providing
re-training, job search assistance and BP's severance package.
BP intends to continue servicing its customers with a range of
tubular LDPE products supplied under third party agreements, in
addition to its new C6 linear low-density polyethylene (LLDPE)
grades made at its Grangemouth, Scotland plant and C4 LLDPE and
autoclave LDPE from the company's Erdoelchemie plant in Dormagen,
Germany. BP also intends to continue supplying its Masterbatch
grades.
The Wilton plant, built in 1973, uses high-pressure autoclave
technology to manufacture low-density polyethylene for use by
customers in a wide range of products such as film applications. BP acquired the plant from
ICI in 1982. 、