| BASF's new segment structure (Effective January 1, 2008) |
 |
BASF plans transformation
into a European Company (SE)
Hambrecht: “Affirmation of an entrepreneurial
vision of Europe”
The Board of
Executive Directors and Supervisory Board of BASF
Aktiengesellschaft have resolved to propose to the Annual Meeting
on April 26, 2007 the transformation of BASF Aktiengesellschaft
into a European Company (Societas Europaea, SE) with the name
BASF SE. The company’s headquarters and chief
administrative offices will remain in Ludwigshafen, Germany.
“The European
Company is a modern legal form for a global company whose home
market is in Europe,” said Dr. Jurgen Hambrecht,
Chairman of the Board of Executive Directors of BASF
Aktiengesellschaft. The transformation into a European Company is
intended to further strengthen corporate governance at BASF. “BASF considers this legal form to
be an affirmation of an entrepreneurial vision of Europe. BASF is
strengthening the participation of European employees in the
company and thus demonstrates its pioneering role in the European
chemical industry.”
BASF’s shareholders will be provided
with more detailed information on transformation of the company’s legal form in the invitation to
the Annual Meeting, which will be sent out as of March 16, 2007.
Europe is BASF’s home market: In 2006, it posted
approximately 60 percent of its sales and employed around
two-thirds of its global workforce of more than 95,000 employees
in the region.
「欧州会社」とは2004年10月以降、EUで設立が可能となったもので、EU法に基づき設立される。正式名称はラテン語でソシエタス・ヨーロピアで通称は‘SE’。 欧州会社は登録住所の置かれた加盟国において登録され、他の加盟国では子会社を設立することなしに活動できる。
また、法的制限を伴うことなく欧州域内のリストラクチャリング、事業再編および事業統合を柔軟に行うことが可能となる。
更に、子会社の場合は親会社又は他の子会社との取引では付加価値税(VAT)が課せられるが、欧州企業の場合は社内取引となるためVATは課せられないというメリットもある。
BASF Breaks Ground In
China For Two New Manufacturing Plants
BASF broke ground for two
new plants in Pudong, near Shanghai in China, which will
manufacture polyacrylate polymers and specialty
chemicals for leather tanning. The plants will provide
customers in the growing Chinese market with a reliable supply of
high-quality chemicals. The two facilities are expected to be
completed in the first quarter of 2008. Investment details were
not disclosed.
The polyacrylate polymers plant will have a minimum capacity of 30,000 metric tons per year, while the plant for
specialty chemicals for leather tanning will have a minimum
annual capacity of 12,000 metric tons of products in liquid or powder
form. A spray dryer with a capacity of 10,000 metric tons per
year is part of the investment. The new plants will be located
next to BASF’s existing facilities for
polyacrylate polymers and leather chemicals in Pudong. 浦東
The polyacrylate
polymers marketed under the trademark Sokalan(R) are synthetic water-soluble
polymers 水溶性ポリマーused in the laundry, paper, water
treatment and textile industries. The specialty chemicals for
leather tanning carry the trademarks Basyntan(R), Relugan(R) and
Tamol(R).
BASF today (March 20, 2007) also inaugurated its polyisocyanate
plant at the
Shanghai Chemical Industrial Park in Caojing, which will serve
the entire Asia Pacific market. The plant has an annual capacity
of 8,000
metric tons
and its product is marketed under the trademark Basonat(R).
Construction work began in June 2005. Polyisocyanates are raw
materials used in the manufacture of automotive, industrial and
wood paints.
BASF 2004/8/31
BASF plans to invest in a polyurethanes specialties site in Shanghai・Site in Pudong, Shanghai establishes a new level of closeness to customers
・System house, product development and TPU production at a single site
・Chinese polyurethanes market expected to grow by about 10 percent per year in the next 10 years
BASF and Monsanto
Announce R&D and Commercialization Collaboration Agreement in
Plant Biotechnology
・Agreement
aimed at developing higher-yielding crops that are more tolerant
to adverse environmental conditions such as drought
・Potential
$1.5 billion/Euro1.2 billion devoted to joint pipeline over life
of the collaboration
・First
products to be commercialized in the first half of the next
decade
BASF and Monsanto Company today announced a long-term joint
research and development (R&D) and commercialization
collaboration
in plant
biotechnology
that will focus on the development of high yielding crops and
crops that are more tolerant to adverse environmental conditions
such as drought. The collaboration is effective immediately.
Under this
collaboration:
| ・ | The companies will establish and collaboratively manage a dedicated pipeline that will focus on the development of crops with higher yields and crops that lead to consistent yields under adverse environmental conditions, such as drought. |
| ・ | Each company will additionally maintain independent trait discovery programs. |
| ・ | From the various programs, each company will nominate specific candidate genes and the most promising candidates will be advanced for accelerated joint development and for commercialization in the Monsanto pipeline. |
| ・ | The two companies expect to generate a greater number of viable research projects than they could have done on their own, accelerate the development of new products, and bring a greater number of traits to the market at a faster speed. |
| ・ | The nominated projects will be jointly funded at a 50-50 cost sharing through each phase of development as the candidate gene works its way toward commercial status. |
| ・ | Products that emerge from the joint development will be commercialized by Monsanto. The companies have agreed to share profits associated with commercialized products, with Monsanto receiving 60 percent of net profits and BASF receiving 40 percent of net profits. |
About Monsanto
Monsanto is an agriculture company. The
company is a leading provider of technology-based solutions and
agricultural products that improve farm productivity and food
quality. Monsanto is committed to investing in products that can
make a difference for its farmer customers and the land they
farm. The company uses plant breeding, plant biotechnology and
other applications of modern science to support its commitment to
agriculture and the farmers that feed, clothe and fuel our
growing world. For more information on Monsanto, see www.monsanto.com.
2006/6/15 http://www.juno.dti.ne.jp/~tkitaba/gmo/news/06061501.htm
BASF Plant Science 干ばつ耐性GM小麦を豪分子植物育種研究センターと共同開発
ドイツの巨大化学企業・BASFが6月8日、モンサント、シンジェンタと並び遺伝子組み換え(GM)作物の開発で世界をリードするその農業部門・BASF Plant Scienceとオーストラリア分子植物育種協同研究センター(MPBCRC)との協力関係を拡充すると発表した。今後7年間に2800万ドルを投資、オーストラリアでの干ばつ耐性や真菌病抵抗性のGM小麦を共同開発するという。
共同研究プログラムの一環として、BASF Plant Scienceは収量増加・干ばつ耐性・真菌病抵抗性の候補遺伝子の大規模なコレクションを利用可能にする。MPBCRCは、典型的な農業条件の下で高度に有効な遺伝子組み換えのための専門知識と特許を持つ技術を提供する。
BASFによると、小麦は、世界で栽培されるトウモロコシに次ぐ穀物であるが、長期化する干ばつが、オーストラリアなどの乾燥地域のみならず、ヨーロッパでも二桁(%で)の収量損失を引き起こしている。また、真菌病も収量を大きく減少させている。真菌病に抵抗性をもつGM小麦は農民の一層有効な作物保護に役立つだろうという。
オーストラリアの2002年の小麦収量は、100年来と言われる干ばつで半減した。その後も、これほど厳しくはないとしても、ほとんど連年の干ばつに見舞われている。今年も多くの農業者が作付できず、牧草も枯れ始めている。こうした傾向は、今後ますます強まるだろう。
BASF to debottleneck Antwerp cracker mid Aug to end Sep
Germany's BASF has
divulged the dates of its planned debottlenecking of its naphtha steam
cracker at Antwerp, Belgium. "The turnaround will start
in the middle of August and last until the end of
September," a company source said Friday.
The Eur200 million ($246 mil) expansion project would make the
plant the largest single-train steam cracker in Europe by boosting its
ethylene capacity from 800,000 mt/yr to 1.08 mil mt/yr.
BASF opens new engineering plastics compounding plant in Shanghai
BASF today celebrated the
inauguration of its engineering plastics compounding
plant at its
Pudong
site in Shanghai,
China. The new facility came on stream in March 2007 and is a
world-scale plant with an annual capacity of 45,000
metric tons.
It is one of the most modern compounding plants in the world
today, with the highest environmental standards and the most
efficient production capabilities available.
Alongside this new plant in Shanghai, BASF has similar
compounding facilities in Malaysia and Korea, which are part of BASF's global
network of engineering plastics and compounding plants. This
network covers other countries in Europe, North and Central
America. With the new plant, BASF's total compounding
capacity in Asia exceeds 100,000 metric tons per annum.
2007/6/12 BASF
BASF considers construction of MDI plant in Chongqing
Plant to have world-scale capacity of 400 kt/a crude MDI
Startup planned from 2010 onward
Investment underlines BASF commitment to China
BASF is considering the construction of a new MDI
(diphenylmethane diisocyanate) plant in Chongqing municipality,
Western China, to meet growing demand for this product. A
corresponding memorandum of cooperation was signed today (June
12, 2007) with Chongqing Chemical and
Pharmaceutical Holding (Group) Company 重慶化醫集團and local authorities. BASF will
now carry out an in-depth evaluation of the competitiveness of
the location. The startup is planned from 2010 onward, and the
plant is expected to have a capacity of 400,000 metric tons
per year of crude MDI.
BASF already announced in early 2006 that it was considering
building another MDI plant in China with
partners.
The
decision on BASF’s additional joint
venture partners has not yet been made, and the final choice of a site
for the plant still hinges on a number of factors.
2006/11/2
BASF
BASF to mothball THF plant in Caojing, China
・Tough market conditions
・Reliable supply to customers
maintained
BASF has decided to mothball its tetrahydrofuran
(THF) plant in Caojing, Shanghai, China. The plant has an annual capacity
of 80,000 metric tons and supplies the raw material THF to the
polytetrahydrofuran (PolyTHF) manufacturing plant at the same
site. The mothballing of the THF plant will start in the first
quarter of 2007, and the PolyTHF plant will be supplied in the
future from BASF’s global production network.
The THF plant was shut down for technical reasons after a salt
leakage in the first quarter of 2006 and has not been started up
since then.
The restructuring will
enhance efficiency, strengthen competitiveness and lead to a further
increase in the capacity utilization of BASF’s THF plants in Germany, USA,
Korea and Malaysia.
Apart from the plant in Caojing, BASF produces PolyTHF at its
sites in Ludwigshafen, Germany, Geismar, USA, and Ulsan, Korea, supplying textile manufacturers
all over the world.
PolyTHF is an important component in the production of elastic spandex
fibers for
textiles such as sportswear, swimwear, underwear and outerwear.
In addition to its role in textiles, PolyTHF is also an important
intermediate for thermoplastic polyurethanes (TPU), which are used for example in
the manufacture of highly abrasion-resistant, yet flexible hoses,
films and cable sheathing.
BASF Agrees to Sell its Minority Ownership Interest in Geismar, LA Ethane Cracker and Associated Facilities
BASF Corporation today
announced that it has agreed to sell its minority
ownership interest in a 610,000 tons per year ethane cracker and
associated pipeline and storage facilities located in Geismar, Louisiana.
Subject to regulatory approvals, Williams Olefins,
L.L.C., will
purchase BASF's ownership interest in the cracker and PetroLogistics,
LLC, will
purchase BASF's interest in the associated pipeline and storage
facilities. Terms of the agreements were not disclosed. Closing
is expected to take place in July. The ethane cracker is jointly
owned by GE Petrochemicals, Williams
Olefins, L.L.C. and BASF, and operated by Williams Olefins,
L.L.C. The pipeline and storage facilities are jointly owned by
GE Petrochemicals, PetroLogistics, LLC, and BASF, and operated by
PetroLogistics.
BASF purchased its ownership stake in the cracker and associated
facilities in 1970 as part of its acquisition of
Wyandotte Chemicals.
Each owner supplies raw materials to the cracker and
independently markets its share of production from the cracker.
"BASF's strategy to more closely balance olefins supply
capability with captive demand is well served by our
world-scale joint venture naphtha steam cracker in Port Arthur,
Texas, reducing the strategic importance
of the Geismar ethane cracker to BASF," said Peter Cella,
NAFTA Group Vice President, Petrochemicals. "We believe our
investment in the Port Arthur cracker and the latest technology
deployed at this facility will provide BASF with a sustainable
first quartile competitive position in the marketplace."
Williams Olefins, L.L.C
Williams' businesses produce, gather, process and transport clean-burning natural gas to heat homes and power electric generation across the country.
Williams has been in business since 1908, when two Williams brothers began a construction company. That business grew into the world's leading pipeline engineering and construction firm. Under the Williams Brothers name, the company went public in 1957 with a net worth of about $8 million.
Williams Olefins, a business unit of Williams, is the operator of the jointly owned world class ethylene production facility located near Geismar, La., where approximately 1.2 billion pounds of polymer grade ethylene and 90 million pounds of polymer grade propylene are produced annually.
BASF/Atofina (60:40 JV)
Port Arthur, Texas
2,000百万lbs
BASF rules itself out of ICI acquisition
The German
chemicals group BASF has told Dutch newspapers it is not
interested in purchasing chemical firms, including ICI, as they
are too expensive.
Board member Stefan Marcinowski told Dutch daily newspaper Het
Financieele Dagblad that acquiring other chemical companies
is not 'financially viable'.
BASF evaluates strategic options for selected styrenics activities
BASF Aktiengesellschaft
(BASF), Ludwigshafen, announced today (July 17, 2007) that it is evaluating
strategic options for selected parts of its styrenics activities. In parallel to the evaluation
process, BASF has received an initial offer for selected parts of
its styrenics activities, and plans to start discussions with the
interested party.
BASF’s activities under consideration
include its styrene monomer (SM), polystyrene
(PS), styrene butadiene copolymer (SBC) and acrylonitrile
butadiene styrene (ABS) businesses with plants in Antwerp, Belgium;
Altamira, Mexico; São José
dos Campos, Brazil;
Ulsan, South Korea; and Dahej, India. These activities posted
sales of about Euro3.2 billion in 2006 and have approximately
1,000 employees.
Hans W. Reiners,
President of BASF’s Styrenics division, said that
BASF’s remaining styrenics activities
will in the future focus on foams and specialties for
the construction, automobile, packaging, sport and leisure
industries. “This ties in with the strategy of
BASF’s Plastics segment to supply its
customers with highly innovative, tailor-made solutions.”
In South Korea, BASF owns a 300,000 mt/year SM plant, a 250,000 mt/year ABS plant, a 320,000 mt/year PS plant and a 65,000 mt/year EPS plant at Ulsan. It procures its required benzene from other producers in Korea and Japan. (Platts)
--------------
2007/8/1 Platts
Germany's BASF in constructive talks with buyer for styrenics:CEO
BASF is in "fairly constructive talks" with one potential buyer for selected styrenics activities, Jurgen Hambrecht, CEO of the Ludwigshafen-based company, said Wednesday during the presentation of Q2 results.
--------------
Plast europe 2007/8/29
Basell : Leading contender for BASF styrenics?
Basell is being touted as a leading contender to acquire the EUR 3.2 bn styrenics activities that BASF put up for sale in July.
German press reports say that BASF and its former 50:50 joint venture (with Shell) have been in talks (now stalled) about a takeover. Both companies have declined to comment on the reports pointing to differing views about the value of the business as well as internal differences at BASF.Financial Times Deutschland
2007/8/6
BASF
BASF to increase
propionic acid capacity in Ludwigshafen and Nanjing プロピオン酸
BASF is increasing
its annual production capacity for the chemical intermediate
propionic acid at its sites in Ludwigshafen and Nanjing by 30,000 metric tons
and 9,000 metric tons, respectively. Production in
Nanjing is ensured by BASF YPC Co. Ltd., a joint venture owned by
BASF and the China Petroleum & Chemical Corporation (Sinopec
Corp.). Once the expansion of the two production facilities is
completed ? in Nanjing and in Ludwigshafen by mid-2009 ? BASF
will have the capacity to make 149,000 metric
tons of
propionic acid each year.
Ludwigshafen 80,000+30,000→110,000
Nanjing 30,000+ 9,000→ 39,000
Propionic acid inhibits the growth of mold and some bacteria and is used as a preservative for animal feed and food for human consumption. The acid is also widely used in the production of vitamin E, pharmaceutical-active ingredients, crop protection agents and solvents.
2007/8/27 BASF
BASF Catalysts expands auto catalyst plants in China and India
Rapidly growing demand in automotive industry
BASF Catalysts is expanding its automotive catalyst plants in Shanghai, China, and Chennai, India, to meet growing customer demand
over the next few years. BASF Catalysts already is a market
leader in automotive catalysts throughout Asia, and the planned
expansions will support the company’s continued leadership in the
region.
In response, BASF Catalysts will nearly double
manufacturing capacity in Shanghai, and triple capacity in
Chennai.
Both sites’ technical capabilities will also
be upgraded in order to deliver the most advanced
emission-control technologies that will meet anticipated new
emissions standards in China and India. Capacity expansions at
both locations will be complete by early 2009.
BASF ready to take out 10 bln eur in debt to finance acquisitions - CFO
BASF AG is ready to take out about 10 bln eur in additional debt to finance acquisitions, less than a year after buying catalyst maker Engelhard Corp, the Germany company's chief financial officer Kurt Bock told the Wall Street Journal Europe in an interview.
BASF is 'underleveraged' and could 'easily' double debt to twice its operating profit, adding about 10 bln eur to acquisition funding, Bock said, according to the newspaper.
BASF increases ethylene oxide capacity in Europe for EO derivatives
BASF is at the moment
successively increasing its production capacity for ethylene
oxide at its Ludwigshafen and Antwerp sites. Most of the work
will be performed during the next planned shutdowns in 2008 and
2009. This will increase BASF’s capacity for ethylene oxide in
Europe from 705,000 to 845,000 metric
tons per
year. A total of 345,000 metric tons per year will
be produced in Ludwigshafen and a further 500,000 metric tons per
year in Antwerp.
BASF mainly
produces ethylene oxide for its own use. The most important
derivatives of ethylene oxide are surfactants,
ethanolamines, glycol ethers and polyols.
“Germany
and China - Moving Ahead Together” in Nanjing:
BASF presents innovative products
and solutions for sustainable development
| ・ | Pavilion featuring energy-efficient and environmentally friendly solutions for housing and the automotive industry plus a Kids’ Lab |
| ・ | High-level corporate social responsibility round table |
| ・ | BASF to sponsor Nanjing taxis with its Keropur(R) fuel additive |
| ・ | Expert symposium on city life and construction |
BASF, Official Partner of
the “Germany and China - Moving Ahead
Together” initiative, today announced its
contributions to the first station in Nanjing, capital of Jiangsu
Province. The initiative will run from autumn 2007 to 2010 and
will tour a number of major cities throughout China to promote
technological and cultural aspects of Germany. BASF’s most visible activity will be a
pavilion on the Germany Esplanade in Nanjing that will be open to
the public from October 19 to 27, 2007. Other activities include
a high-level corporate social responsibility (CSR) round table,
the sponsorship of Nanjing taxis with BASF’s Keropur(R) fuel additive, and an
expert symposium on city life and construction.
| BASF
Pavilion: Construction and living, mobility and Kids’
Lab The pavilion will feature three main areas: |
|
| ・ | In the “low-energy apartment” BASF will show how its innovative products for the construction industry reduce both energy consumption and emissions while enabling a modern lifestyle. In addition, there will be hands-on exhibits related to topics such as smart temperature management, sound absorption and heat-reflecting surfaces. |
| ・ | The second area focuses on how BASF helps to make cars more environmentally friendly with a wide range of solutions for the automotive industry. Exhibits include water-based coatings and emission-control catalysts, as well as plastics that reduce the weight of cars and cut fuel consumption. |
| ・ | Finally, the pavilion will contain a Kids’ Lab in which children aged between 6 and 12 years can discover the world of chemistry through exciting specially designed experiments. Here again, two of the six experiments deal with aspects of environmental protection: wastepaper recycling and wastewater purification. |
BASF inaugurates two new plants at its Freeport, Texas, site
BASF today (October 8,
2007) inaugurated two new manufacturing plants at its site in
Freeport, Texas - a production line for polyamide 6
(nylon) and a plant for superabsorbent
polymers (SAP).
The polyamide production line replaces a
facility in Enka, North Carolina. The new line has an annual capacity
of 120,000 metric tons per year, and the caprolactam
feedstock is supplied by another BASF plant at the Freeport site.
The new superabsorbent polymers manufacturing facility
is supplied with a key raw material, acrylic acid, from another
BASF plant at the Freeport site which provides major competitive
advantages in terms of logistics and product quality. The new SAP
plant has a capacity of 180,000 metric tons per year and replaces existing
facilities in Aberdeen, Mississippi and Portsmouth, Virginia.
BASF further expands its position for engineering plastics in Europe
BASF has signed an agreement with SABIC Innovative Plastics on the acquisition of SABIC Innovative Plastics'shares in the PBT joint venture, BASF GE Schwarzheide GmbH & Co. KG. PBT (polybutylene terephthalate) is an engineering plastic.
BASF has a proven track record in Europe with firms who have co-located at the company’s two major German sites --Ludwigshafen and Schwarzheide.
JV with GE Plastics thrives at BASF’s Schwarzheide site
In 1997, General Electric’s GE Plastics Europe BV and BASF AG teamed up to create BASF GE Schwarzheide GmbH & Co., a 50/50 joint venture that manufactures and markets polybutylene terephthalate (PBT), a thermoplastic polyester used in auto components, appliances and consumer products. When the new company sought a home for its world-scale 60,000 tonne per year facility, it looked at several options. The company decided to co-locate at BASF’s Schwarzheide site because of the cost advantages there and the fact that a compounding facility was already on site. Today, the joint venture is the largest customer for services at the Schwarzheide site. The BASF GE venture is integrated into the whole energy structure of the site, and pays for site services as they would anywhere else. Executives at BASF GE Schwarzheide describe the investment as a success and consider it a well-run operation.
The purchase of SABIC Innovative Plastics'shares in BASF GE Schwarzheide marks BASF’s fifth acquisition in the sector of engineering plastics within the last five years. In 2003, Honeywell’s worldwide engineering plastics business and Ticona’s polyamide 66 business were bought and have been successfully integrated. This was followed in 2005 by the takeover of Leuna-Miramid GmbH and the engineering plastics business of LATI USA Inc. Moreover, BASF has started up operations in the growth market of Asia within the last 18 months, including a new production joint venture for PBT together with Toray in Malaysia and a new compounding plant in Pudong near Shanghai, China.
May 22, 2006
More polyamide specialties
- Leuna-Miramid to be renamed BASF Leuna
- New brand concept for BASF's polyamide plastic
Leuna-Miramid GmbH - a manufacturer of special polyamide compounds at the chemical site in Leuna, Germany - which was taken over by BASF in November 2005, is to be renamed BASF Leuna GmbH. The name change reflects the complete incorporation of this site into BASF's integrated network (Verbund). The brand name Miramid®, however, will be retained in BASF's product portfolio.
2005/12/8
BASF to acquire major North American engineering plastics business of LATI Engineering plastics portfolio strengthened with additional nylon, PBT, POM resins
BASF Corporation and LATI USA Inc., the U.S. affiliate of the Italian engineering plastics compounder LATI Industria Termoplastici SpA, have reached an agreement in which BASF will acquire the nylon 6 and nylon 6,6, polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) and polyoxymethylene (POM) business of LATI USA Inc., effective December 30, 2005. Financial details of the transaction are not being disclosed.
BASF will not acquire any manufacturing sites, equipment or related assets as part of the transaction. Also, no LATI employees will be transferred to BASF. For a period of time, LATI will supply its nylon (Latamid®, Kelon®, Latilub®, Latiblend®), PBT (Later®) and POM (Latan®) product lines to BASF under a transitional supply and services agreement.
LATI USA Inc. and BASF jointly expressed their commitment to a successful transition and will work closely to support customers to ensure no disruption of product supply and services occurs.
参考 Bayer/GE
Bayer MaterialScience is to transfer EXATEC shares to GE Plastics
Bayer MaterialScience is to transfer its shares in EXATEC to GE Plastics. This transaction will be completed subject to the approval of the relevant antitrust authorities. No statement will be made concerning the financial aspects.
With this decision, Bayer MaterialScience has opted to carry out its own independent development of polycarbonate automotive glazing, a market that is set to enjoy future growth. EXATEC was founded in 1998 as a 50:50 joint venture between Bayer and GE with the aim of developing technologies to produce automotive glazing systems from polycarbonate. gration mean it can also be used for rear windows, and open up further areas of application within the automotive industry.
BASF reorganizes its businesses: Faster to market, closer to customers, increased efficiency and greater cyclical resilience
BASF's new segment structure (Effective January 1, 2008)
BASF expands plasticizers business in Asia Pacific
・Oxo-C4
production capacity in Nanjing to be expanded to 305,000 metric
tons
・Plasticizer
applications laboratory inaugurated in Shanghai
・Focus
on innovative products Hexamoll(R) DINCH and Palatinol(R) 10-P
BASF today (January 9, 2008) outlined several key initiatives for
its Asia Pacific plasticizers business. To meet growing demand
for solvents and plasticizers the company plans to expand the
annual production capacity of its oxo-C4 plant in
Nanjing, China, by 55,000 metric tons to 305,000 metric tons by the fourth quarter of 2008.
This move will ensure reliable supplies of the precursor alcohols
n-butanol and 2-ethylhexanol. In Asia, and in China especially,
demand for plasticizers is expected to grow by 4 to 5 percent per
year through to 2015.
At the same time, BASF inaugurated the region’s first plasticizer
applications laboratory in Shanghai.
February 12, 2008 Thomson
Financial
BASF interested in acquiring Albemarle for 4.9 bln US$
BASF SE is interested in acquiring the US' chemicals company
Albemarle Corp for 4.9 bln usd, a 30 pct premium on its current
market capitalization, Capital reported on its website, not
citing where it got the information.
It said the German chemicals company declined to comment
respective rumours that according to the report were making
rounds on Wall Street.
Albemarle is a client of BASF.
The report said BASF would mostly be interested is Albemarle's
profitable refinery operations, which account for 40 pct of its
sales.
Albemarle Corp
Albemarle Corporation, incorporated in 1993, is a global developer, manufacturer and marketer of highly engineered specialty chemicals. The Company sells a diversified mix of products to a range of customers, including manufacturers of consumer electronics, building and construction materials, automotive parts, packaging, pharmachemicals and agrichemicals, and petroleum refiners. As of March 1, 2007, the Company and its joint ventures operated 43 facilities, including production, research and development facilities in North and South America, Europe, Australia and Asia. It serves more than 3,400 customers in over 100 countries.Albemarle Corporation's operations are managed as three operating segments: Polymer Additives, Catalysts and Fine Chemicals.
Total sales 2,369 million $
Polymer additives 39%:Flame retardants、Antioxidants、Curatives、Stabilizers
Catalysts 35%:FCC、HPC、Polyolefin、Specialty catalysts
Fine chemicals 26%:Fine chemistry services、Pharmaceuticals、Bromine chemicals、Other industrial specialties
BASF secures alternative
raw material supply for polyamide 6.6 business
* BASF and INVISTA enter into ADN supply agreement
* Proposed closure of ADN plant at Seal Sands in early 2009
BASF announced today that it has secured an alternative raw
material supply for its strategically important polyamide
business. BASF will purchase adipodinitrile (ADN) from the global
network of U.S.-based company INVISTA. ADN is used as a raw
material to produce hexamethylenediamine (HMD) at BASF’s Seal Sands site, Teesside, U.K.
HMD is a key intermediate for BASF’s Ultramid A (Polyamide 6.6).
Supply from INVISTA will commence at the start of 2009, and once
a reliable delivery has been established, BASF aims to close and
dismantle its ADN plant in Seals Sands. Both companies will
ensure that customers are not affected by the raw material supply
changes.
BASF is producing Ultramid A (Polyamide 6.6) from the key
intermediates HMD and adipic acid at its site in Ludwigshafen,
Germany. In addition, BASF operates fully backward-integrated
production plants for Polyamide 6 (Ultramid B) at its Verbund
sites in Ludwigshafen, Antwerp, Belgium and Freeport, USA.
Ultramid A and B are used to produce engineering plastics which
go into the automotive, electric&electronics, furniture and
leisure industries. In addition, Polyamide 6 and 6.6 are used to
produce fibers for textile, carpet and industrial applications.
BASF Plant Science and Academia Sinica (Taipei) to cooperate on gene discovery
BASF Plant Science and
Academia Sinica 台湾中央研究院, the leading research institute
in Taiwan, today signed a cooperation agreement. Focus is on the discovery of genes
that increase yield and improve stress tolerance in major crops
such as rice and corn. Financial details have not been
disclosed.
After agreements with CFGC (South Korea) and
NIBS (Beijing),
the agreement with Academia Sinica is the third cooperation
agreement that BASF Plant Sci-ence has entered within the past
eight months. “BASF Plant Science highly values
the quality of work carried out by research institutes in
Asia-Pacific,” said Logemann.
January 24, 2008
BASF
BASF Plant Science and National Institute of Biological Sciences,
Beijing enter cooperation and license agreement
・ BASF
Plant Science intensifies biotech cooperation activities in Asia
Pacific
・ Research
focuses on higher yield in major crops such as corn (maize),
soybeans and rice
BASF Plant Science and
the National Institute of Biological Sciences, Beijing (NIBS) 北京生命科学研究所 today announced a cooperation and
licensing agreement in biotechnology. It is the first cooperation
to be made by BASF Plant Science in the People’s Republic of China and focuses on
increasing yield in staple crops such as corn, soybeans and rice.
About the National Institute of Biological Sciences, Beijing
The National Institute of Biological Sciences, Beijing (NIBS,
Beijing) was established to advance the frontier of basic
research in the life sciences in China. Founded in 2003 as part
of a strategic government initiative to further national
development of science and technology, NIBS aims to become a
first rate, internationally competitive research institution. Its
faculty will educate future generations of life scientists and
explore a new model for operating scientific institutions in
China. NIBS currently has six plant biology laboratories with
focus on research in the mechanisms of plant development and how
plants respond to internal and environmental signals. Many of
their research discoveries have direct implications to
agribiotechnology and improvement of crops.
BASF Plant Science and Crop Functional Genomics Center sign R&D agreement in South Korea
BASF Plant
Science and Crop Functional Genomics Center (CFGC), the
leading Korean consortium for crop research, today
(October 4, 2007) signed a coopera-tion and licensing
agreement in Seoul, South Korea. The agreement includes
the discoveries by 200 top researchers from 40 renowned
research institutes over 10 years. |
| About CFGC: The Ministry of Science and Technology of Korea has developed in 2000 the 21st Century Frontier R & D Program to boost national competitiveness in science and technology, improve the quality of life, and benefit humanity. The Crop Functional Genomics Center (CFGC), which belongs to the program, focuses on the func-tional genomic study for crop improvement. Unraveling the complex relationship between genes and phenotypes and applying this information to the development of better crops are dependent on cooperative works in genomics, transformation, and molecular breeding, and should eventually make a significant contribution to global food security. CFGC is a virtual institution supporting research projects that are carried out in universities, research institutes and industries throughout the nation and about 250 PhD scientists are working for the program. For 10 years of the program pe-riod, the CFGC will run target-oriented basic research and their application pro-jects in the fields of plant functional genomics, crop transformation, and plant mo-lecular breeding. Science and technology have made extraordinary progresses in the last century, contributing tremendously to the improvement of human life. We are among those responsible for leading 21st century science and technology, being convinced that all our goals can be achieved through establishing a new paradigm for global collaboration. To find more about CFGC, please visit our Internet website at: www.cfgc.snu.ac.kr |
BASF delayed styrenics sale because of low offers
BASF SE did not meet its June 30 deadline to sell parts of its styrenics operations because potential buyers were struggling to find funding and were offering too little.
Suitors are facing stricter requirements to provide own equity while interest rates have gone up, BASF chief executive Juergen Hambrecht told analysts at a conference in London.
'We are not selling it under conditions which are not justifiable,' he said, adding the process continues.
In February, the company said it is in negotiations with one party and that it plans to clinch a deal in the first half.
BASF has described the divestment as inevitable, saying standard styrenics will not have enough of an edge over rival products in the long run.
Jul 30, 2008
Reuters
BASF looking at takeover targets
German chemical group BASF is considering taking over U.S. rival W. R. Grace &
Co, the
Financial Times Deutschland said on Wednesday, citing middle
management and banking sources.
As well as assessing Grace, which has $3.1 billion in annual
turnover, BASF will also be looking closely at the strategy,
company structure and business development of U.S. group Rockwood and Germany's Cognis COGN.UL with a view to acquisitions, the
paper said.
All three potential targets have been given project names, a sign
that they are being considered seriously for takeover, the report
said.
2007/9/20 BASF、新しい買収?
W. R. Grace & Co
Grace is a premier specialty chemicals and materials company.
First Choice for Packaging Assurance
Grace Materials and Packaging Technologies provides sealants, coatings and closures to the food and beverage industries that are used in more than 300 billion containers each year.
Worldwide Leader in Construction Products
For more than 50 years, Grace Construction Products has offered commercial and residential construction products used in projects ranging from major infrastructure to minor home repair.
Global Specialty Chemical Supplier
Grace Davison is the second longest continually operating chemical company in the United States, offering discovery sciences, engineered materials, packaging technologies, catalysts and refining technologies.
We help biorefineries manufacture alternatives to gasoline and diesel that promote clean energy sources.グレースケミカルズは米国コンクリート混和剤の最大手メーカーであるW.R.グレースの実績とセメント・特殊混和材メーカーの電気化学工業㈱の開発を結び、多様化するニーズに対応しております。
April 2, 2001
W. R. Grace & Co. today announced that the Company has voluntarily filed for reorganization under Chapter 11 of the United States Bankruptcy Code in response to a sharply increasing number of asbestos claims. This Chapter 11 filing includes 61 of Grace's domestic entities. None of the Company's foreign subsidiaries are included in this filing.
Grace is the sixth major company to cite asbestos claims as their reasons for filing chapter 11 since January. Twenty-six companies have made such filings since 1982.
Rockwood
Rockwood Holdings, Inc. is a world-class specialty chemicals and advanced materials company committed to delivering exceptional value through continued leadership in customer service, quality, on-time delivery and innovative technology and is currently composed of 15 individual business units.
2007 net sales by end-use market
Chemicals and Plastics 13%
Life Science 8%
Electronics and Telecommunications 11%
Consumer Products 4%
Metal Treatment ang General Industrial 16%
Paper 3%
Construction 14%
Specialty Coatings 7%
Automotive 14%
Environmental 2%
Others 8%Cognis COGN.UL
ドイツ・モンハイムに本社を置き、世界30カ国に拠点を持ちます。 油脂化学をバックボーンに、160年に及ぶ経験と実績を有する、世界的な総合化学会社です。自然由来の機能性食品、栄養補助食品素材など健康の向上を目的とする製品、低刺激な化粧品や洗剤、そして塗料・インクなどの原料、が私たちの製品群です。
Cognis is a leading specialty chemicals company with activities around the world. Utilizing its 160 years of experience in oleochemicals, Cognis markets innovative products and solutions for personal care, home care and modern nutrition, as well as high-performance products for numerous industrial markets.
Care Chemicals Nutrition & Health Functional Products PulcraChemicals Cognis Oleochemicals ・Hair / Body / Oral Care
・Home Care
・Industrial & Institutional
Cleaning
・Skin Care
・Silicates・Dietary Supplements
・Pharmaceuticals & Healthcare
・Food Technology
・Functional Food &
Medicamental Nutrition
・Adhesives
・Consumer Coatings
・Emulsion
Polimerization
・Graphic Arts
・Industrial Coatings
・Polymer
Building Blocks
・Synlubes Technology
・AgroSolutions
・Mining Chemicals
・Ion-Transfer Technology・Textile Technology
・Fiber Technology
・Leather Technology
・Fatty Acids
・Glycerin / Triacetin
・Ozon Acids
・Plastic Additives
・Oilfield Chemicals
BASF takes a further step
in the divestment of its styrenic activities![]()
BASF is continuing the
divestment process of its global styrenic business and plans to
reorganize the business into new subsidiaries as appropriate. The new companies
are expected to be established in January 2009.
In addition, the scope of the activities to be sold will be
expanded to include the styrene copolymer business. This expansion includes styrenic
copolymer production plants in Ludwigshafen and Schwarzheide,
Germany as well as the styrene copolymer global marketing, sales
and logistics activities.
The new subsidiaries will operate the global styrenics business
independently. They will combine the commodities styrene monomers
(SM), polystyrene (PS),
styrene butadiene copolymer (SBS) and acrylonitrile butadiene
styrene (ABS) as
well as the styrene copolymers consisting of the Luran®
(SAN), Luran®
HH (AMSAN), Luran®
S (ASA), Terblend®
N (ABS/PA),
Terluran® HH (ABS-HH), Terlux®
(MABS) and
Styroflex® (SBS) brands. The styrenic
commodities and copolymers with around 1,600 employees had total
sales of about Euro 4 billion in 2007 and production sites
located in Antwerp, Belgium; Ludwigshafen and
Schwarzheide, Germany; Altamira, Mexico; São José dos Campos,
Brazil; Dahej, India; and Ulsan, South Korea. BASF will concentrate its
remaining styrenic plastics activities on its foams business
for the construction and packaging industries as part of the
Performance Polymers division.
commodities
SM
PS
SBS スチレン-ブタジエン-スチレンブロック共重合体
ABS
コポリマー
Luran®
(SAN) スチレン/アクリロニトリル
コポリマー
Luran®
HH (AMSAN) α-Methylstyrene-acrylonitrile copolymers
Luran®
S (ASA) styrene acrylonitrile copolymers that have
been impact-modified with acrylic ester rubber
Terblend®
N (ABS/PA)
Terluran®
HH (ABS-HH) (High Heat:modified ABS that meets the requirements
for thermally stressed components)
Terlux®
(MABS) Methyl methacrylate-acrylonitrile-
butadiene-styrene-polymer
Styroflex®
(SBS) Styrene/butadiene
block copolymer
2008/9/15 BASF
BASF makes offer to acquire Ciba
* Cash offer of CHF 50.00 per share provides attractive premium
* Ciba’s Board of Directors supports
offer
* BASF to expand its leading position in specialty chemicals with
additional products and services
* Repositioning and restructuring of paper chemicals operations
to create leading supplier with extensive portfolio
* Basel to remain an important site for parts of the combined
business
* Conference call at 9:00 a.m. CEST, press conference in Zurich
at 11:00 a.m.
BASF plans to acquire Ciba Holding AG, Basel, Switzerland, a leading
specialty chemical company, and will make a public takeover offer
to Ciba’s shareholders. BASF will pay CHF
50.00 in cash for each nominal share in Ciba. BASF and Ciba have
reached a transaction agreement in which the Board of Directors
of Ciba supports BASF’s attractive offer and recommends
its acceptance to Ciba’s shareholders. The offer
corresponds to a premium of 32 percent above the closing price
for Ciba’s shares on September 12, 2008 and
a premium of 60 percent above the volume-weighted average share
price for Ciba shares in the 30 days prior to announcement of the
public takeover offer. Based on all outstanding Ciba shares and
including all net financial liabilities and pension obligations,
the enterprise value would be CHF 6.1 billion (approximately Euro 3.8 billion).
2008/9/15 polymer-age.co.uk/
The acquisition of Ciba would benefit BASF on a number of fronts.
In plastics Ciba's additives business would augment BASF's own, particularly with the addition of UV stabilisers and antioxidants, and expand the total plastics materials package it is able to offer. Allied to this is Ciba's strong position in coating effects which would also extend BASF's existing range.
Both companies are significant players in paper chemicals, although Ciba has had difficulty in maintaining adequate profitability, and said in August that it was "considering options" for the future of the business. Combining the two businesses would create a market leader, and enable the "extensive restructuring" that BASF sees as needed.
Ciba has a strong position in water treatment chemicals, which would boost BASF's own operations in this area.
As well as the sectorial benefits from combining the two companies, there are geographic and strategic advantages. BASF is a global chemicals company, but the addition of Ciba's portfolio, particularly in water purification, gives it potential to increase its presence in emerging economies. And BASF's global presence offers more potential for Ciba's niche market businesses, such as oil and mining. The two companies also complement each other in research and development, and the merger would bring to Ciba the advantages of BASF's upstream materials integration.
As part of its offer terms BASF has made assurances over the future of Ciba sites in Switzerland and says it will set up an operating division with global responsibilities in Basel.チバ・ジャパンは16日、BASFからチバ・ホールディングAG のすべての発行済株式を一株当り50スイスフランで公開買付するとの提案を受けたと発表した。
チバは、プラスチック添加剤、コーティング機能材、製紙・水処理剤における卓越したイノベーション能力とアプリケーションの専門的知見を通して、スペシャライズド・ケミカル・エンジニアリングの分野で、BASFの戦略とオペレーションを強化する。
同時に、BASFのグローバルな研究、生産、マーケティング基盤とともに、重要な原材料および中間体についての共同後方統合は、チバにとって大きなメリットとなる。両社は、これまで長期にわたり、広範囲なサプライヤーと顧客の関係を維持してきた。Public tender offer by BASF for Ciba
* Board of Directors of Ciba recommends shareholders accept offer * Industrial logic: Integration into BASF will strengthen Ciba’s businesses through access to BASF’s global research, production and marketing platform, raw materials and intermediates * Commitment to strategically important production sites in Switzerland and R&D site in Basel * Fair price for shareholders Ciba strengthens BASF’s strategy and operations in the field of specialized chemical engineering through its leading innovation capabilities and application expertise in Plastics Additives, Coating Effects and Water & Paper Treatment. At the same time, Ciba benefits from BASF’s global research, production and marketing platform, as well as the associated backward integration into important raw materials and intermediates. The two companies already maintain long-standing and extensive supplier and client relationships.
Bacteria-free surfaces
BASF's new Luran®
S BX 13042 kills
bacteria
First antimicrobial BASF plastic
BASF is now offering a
plastic that has the property of killing microbes. This material
belongs to the specialties found in the styrene plastic product
line. It goes by the name Luran® S BX 13042 and is currently the
only ASA (acrylonitrile-styrene-acrylate copolymer) with an
antimicrobial effect. The product will be presented at the FAKUMA
2008 in October in Friedrichshafen, Germany. Sample amounts are
already available in the color white.
The antimicrobial material contains silver compounds that are
incorporated into the plastic in order to impart its surface with
a germicidal effect. Interesting areas of application for this
material are not only hand dryers, soap dispensers or entire
sanitary units in public washroom facilities, but also other
products that come into contact with bacteria and other
microorganisms and that need to be sterile such as, for instance,
hospital beds, medical treatment chairs or computer keyboards in
public offices. The combination with the classic ASA properties
such as weathering resistance, high thermal-ageing stability,
good chemical resistance and outstanding surface quality yields a
new material with an extraordinary property profile.
BASF looking to sell its
shares in PEC-Rhin
BASF SE intends to sell its 50 percent holding in PEC-Rhin. PEC-Rhin is a 50-50 joint
venture between BASF SE and GPN. The company produces ammonia, nitric
acid and fertilizers in Ottmarsheim, France.
BASF's fertilizer business currently comprises production
activities in Ludwigshafen (Germany), Antwerp (Belgium) and
Ottmarsheim (France).
In contrast to Ottmarsheim, the fertilizer activities in
Ludwigshafen and Antwerp are based on Verbund integration with
other value chains.
PEC-Rhin was founded in 1967. The joint venture has a workforce
of about 200 employees and in 2007 generated sales in the low
three-digit million Euro range.
BASF reduces production
worldwide
*
Massive decline in demand in key industries
*
Previous year’s earnings level will not be
achieved
BASF is taking measures to avoid the creation of overcapacities
as a result of a massive decline in demand. The company is
temporarily shutting down around 80 plants
worldwide. In
addition, BASF is reducing production at
approximately 100 plants. This was already announced for
polystyrene and caprolactam. Scheduled maintenance work is being
brought forward.
“We
already drew attention to the difficult economic situation at the end of
October.
Since then, customer demand in key markets has declined
significantly,” said Dr. Jurgen Hambrecht,
Chairman of the Board of Executive Directors of BASF SE. “In particular, customers in the
automotive industry have canceled orders at short notice.”
In addition, sales
volumes are being negatively impacted by increased
reduction of inventory by customers and a lack of credit in
customer industries.
“In
2008, BASF will therefore not achieve the previous year’s excellent EBIT before special
items. How the coming year will develop is difficult to foresee.
BASF is preparing for tough times,” said Hambrecht.
BASF abandoned its goal of matching last year's 7.61 billion euros ($9.6 billion) in operating profit
The adjustments are primarily being carried out in units that supply the automotive, construction and textile industries.
Production will be reduced at a further 100 factories, including a site in Malaysia, BASF said. Forty factories in the company's industrial hometown in the Rhineland-Palatinate region of Germany will be idled, as well as 10 in North America and 15 in Asia, spokesman Daniel Pepitone said. U.S. closures include factories in Geismar, Louisiana, and Freeport, Texas, that make dispersions ディスパージョン製品and toluene diisocyanate, or TDI, used in foams and adhesives. An ethylene plant in Port Arthur, Texas, is running at reduced capacity, Pepitone said.
The capacity reduction is to last until January for individual plants and may continue with shorter working times after that, should weak demand continue, the company said.
`BASF is preparing for tough times,'' Hambrecht said. ``Going forward visibility isn't as clear as we'd like. It's like driving into fog and you can't see very far in front of you,'' he said.
BASF Halts Plan to Move Styrenics Business Into New Subsidiary
BASF SE, the world's biggest chemical producer, abandoned plans to move its styrenics businesses into new subsidiaries after the company couldn't find a buyer.
BASF will reexamine options for styrenics and the business will remain within the company instead of being separated on Jan. 1 as originally planned, the Ludwigshafen, Germany-based company said in a newspaper for employees.
2009/1/15 BASF
BASF to change PolyTHF feedstock supply in Korea
* Shutdown of local BDO and THF production
* Local PolyTHF production will continue to operate
* Supply of BDO and THF to customers will continue via global
network
BASF plans to permanently close its production facility for
1,4-butanediol (BDO) and tetrahydrofuran (THF) in Ulsan, which
has been temporarily shut down since August 2008, and the company
will continue to supply related customers via its global network.
BASF's PolyTHF plant in Ulsan will continue to operate with
feedstock from the network accordingly.
BASF will continue to maintain a reliable supply of BDO and THF
to its PolyTHF plant at Ulsan from BASF's global network,
including the company's THF plant in Caojing, China, which is
operating with a new BASF-owned technology.
BASF produces THF at its plants in Ludwigshafen (Germany), Geismar (USA), Caojing (China) and Kuantan (Malaysia). With BDO produced at these plants and at BASF's Chiba (Japan) site, the total global capacity for BDO equivalents amounts to 535.000 metric tons per year. In addition to Ulsan, BASF produces PolyTHF in Ludwigshafen, Geismar and Caojing with an annual capacity of 185.000 metric tons.
Both units have been temporarily closed since August 2008 to help the company cope with the ongoing economic downturn, which has caused severe drops in demand for many chemicals. BASF says that under current conditions it cannot produce BDO and THF at the plant at competitive prices. 27 jobs will be affected, the company says.
| BDO | THF | PolyTHF | ||
| Ulsan (Korea) | ○→X | ○→X | ○ | |
| Ludwigshafen (Germany) | ○ | ○ | ○ | |
| Feluy (Belgium) | ○→X | 2005年停止 | ||
| Geismar (USA) | ○ | ○ | ○ | |
| Caojing (China) | ◎ | ○ | ○ | 当初は独自の新技術でブタンから直接THF製造 技術的問題からTHF停止、その後改造してBDOから製造 |
| Kuantan (Malaysia) | ○ | ○ | BASF Petrobras | |
| 千葉 | ○ | BASF千葉:BASF 67%(当初は50/50の出光BASF) | ||
| 四日市 | ○→X | ○→X | 2006年停止 |
BASF got environmental
approval for MDI project in Chongqing
On Jan. 12, 2009, BASF got environmental approval from China?s
Ministry of Environment Protection (MEP) for its proposed MDI
project in Chongqing Chemical Industry Park (CCIP), Changshou,
Chongqing.
The total investment is USD 1.18 billion (RMB 8 billion), among
them, the investment for environment protection is USD 102
million (RMB 696 million). The project includes 400,000 t/a
nitrobenzene, 300,000 t/a aniline, 400,000 t/a crude MDI and
refining facility, 20,000 t/a MDI pre-polymer, storage facility
and other utilities.
According the BASF, the MDI project will use the most advanced
technologies in environmental protection and met China's standard
for discharge of pollutants.
BASF has announced a world-scale capacity of 400 kt/a crude MDI
in Chongqing, to meet growing demand for this product in China. A
corresponding memorandum of cooperation was signed in Jun. 2007
with Chongqing Chemical and Pharmaceutical Holding (Group)
Company and local authorities.
Orginally, BASF announce the startup is planned from 2010 onward
depending on the time of approval, but now, the project is
expected to start up in 2012.
2008/10/13 BASFの重慶MDI計画,進展か
BASFは上海に、ハンツマン、上海クロルアルカリ、上海華誼、シノペック上海高橋化学と共同でイソシアネートコンプレックスを建設、TDI
16万トン、粗MDI 24万トンを生産し、MDI精製を行っている。
BASFは2006年1月、上記計画の第2弾として、BASF、ハンツマン及び中国側パートナーが中国でのMDI増設を考えていることを明らかにした。
能力はワールドクラスの40万トンで、2010年以降のスタートとし、いくつかの立地を評価しているとしていた。
2007年6月、重慶でMDI工場の建設を検討していること、重慶化醫集団及び市当局との間で協力の覚書を締結したことを明らかにした。
MDI能力は40万トンで、経済性について評価を行っており、2010年以降のスタートを考えているとし、JVの相手はまだ決まっていないとしていた。
環境保護省の情報では、BASFは今回の上記計画を単独で実施する。
BASFは当初、2010年スタートとしていたが、現在では2012年のスタートが予定されている。
なお、更に上流の原料については、協力覚書を締結した重慶化醫集団が供給する。
重慶化醫集団はBASFのMDI計画に合わせ、次の4つの子会社を設立し、昨年8月29日に建設開始の式典を行った。
クロルアルカリ:300千トン(天原化学)
硫酸:400千トン(建峰化学)
フォルムアルデヒド:400千トン(長風化学)
クロロプレンゴム:40千トン(長壽化学)
前3つはMDIの原料で、クロロプレンゴムは塩素を原料に生産するもの。
BASF takes steps to
optimize its structures
*Performance Products segment sharpens focus on customer
industries
*New operating division Paper Chemicals established
*Preparations to integrate Ciba businesses
*BASF reviews strategic options for its leather and textile
chemicals business
Details of the
organizational changes as of April 1, 2009 are as follows:
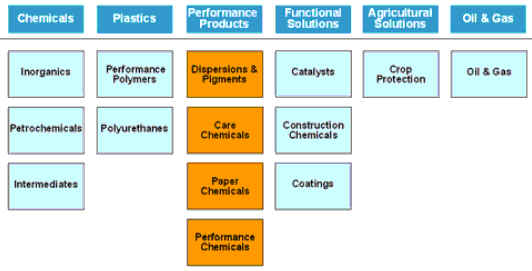
BASF's new segment structure (Effective January 1, 2008)
BASF reviews strategic options for leather and textile chemicals
In addition to implementing this cost-reduction program, BASF is
reviewing future strategic options. In particular, these include
the formation of a joint venture or the complete sale of the
business. “The market requires this step not
just because of the fragmented supplier structure and the low
market growth,” said Reiners.
| 旧所属 | |||
| Performance Products segment | Dispersions
& Pigments ↑ (Acrylics & Dispersions) |
dispersions | Acrylics & Dispersions |
| pigments and coatings resins | Performance Chemicals | ||
| Ciba’s Coating Effects | Ciba | ||
| Care Chemicals | cleaning, personal care and hygiene | ||
| human and animal nutrition | |||
| pharma | |||
| superabsorbents | Acrylics & Dispersions | ||
| Performance Chemicals | plastics processing, automotive, refineries, oil fields and mining | ||
| leather and textiles | |||
| Ciba’s plastics additives | Ciba | ||
| Paper Chemicals (新設) |
paper chemicals business, binders and kaolin minerals | Acrylics & Dispersions | |
| Ciba’s business | Ciba | ||
| Chemicals segment | Petrochemicals | ||
| acrylics (プロピレン誘導品) | Acrylics & Dispersions |
Merger control
authorities approve acquisition of Ciba by BASF
Settlement conditions for tender
offer fulfilled
Transaction to close on April 9
The U.S. Federal Trade Commission (FTC) and the Chinese merger control authority MOFCOM approved the acquisition of Ciba Holding AG by BASF on April 2, 2009. No conditions were imposed beyond those required by the European Commission in its decision of March 12, 2009.
Furthermore, the condition imposed by the European Commission to reach a sales agreement for Ciba's business with the light stabilizer CHIMASSORB 119 FL (HALS) before closing has been fulfilled. The buyer is the Italian company Sabo S.r.l.
CHIMASSORB 119 FL
ヒンダードアミン系光安定剤(HALS)・高分子量タイプ低抽出性、低揮散性を有する高分子量型ヒンダードアミン系安定剤であり、耐NOxガス変色にも優れる。ポリオレフィン系及びスチレン系ポリマーに卓越した性能を発揮する。顔料の凝集作用が少ない。
As a result, the conditions for the settlement of the tender offer are now fulfilled (closing): The offer price of CHF 50.00 per tendered share can be paid and the Ciba shares transferred to BASF.
The planned settlement date is April 9. As of this date, BASF will hold approximately 95.8 percent of Ciba shares. Ciba shares tendered to BASF can be traded on the second line of the SIX Swiss Exchange until April 3, 2009. Ciba shares that have not been tendered can be traded on the SIX Swiss Exchange until further notice.
2009-03-12 EU
Mergers: Commission approves acquisition of Ciba by BASF, subject to conditions
The European Commission has cleared under the EU Merger Regulation the proposed acquisition of Ciba of Switzerland by BASF SE of Germany, both active in the chemicals industry. To remedy competition concerns the Commission had in relation to a number of specialty chemical products, used inter alia in the paper, dyestuffs, plastics and skin care sectors, BASF offered undertakings to divest activities in the sectors in question. In the light of these commitments, the Commission concluded that the proposed transaction would not significantly impede effective competition in the EEA or any substantial part of it.
Competition Commissioner Neelie Kroes commented "I am satisfied that the divestments offered by BASF will ensure that its takeover of Ciba will not harm competition in markets for a range of chemicals used in consumer goods such as skin care products, paper and plastics".
BASF, the ultimate parent company of the BASF Group, headquartered in Ludwigshafen, Germany, is the world’s largest chemical company. BASF is active in chemicals, plastics, performance products, agricultural and nutritional products and oil and gas. Ciba, the ultimate parent company of the Ciba (formerly Ciba Specialty Chemicals) Group, is a specialty chemicals company headquartered in Basel, Switzerland.
The Commission's investigation revealed that the proposed transaction would not significantly modify the structure of the majority of the relevant markets, as a number of credible and more significant competitors would continue to exercise a competitive constraint on the merged entity.
However, the Commission found that the proposed transaction would raise competition concerns in a number of relevant specialised markets, namely
- DMA3 (dimethylaminoethyl acrylate - a chemical intermediate)
- synthetic dry strength agents (used in the paper industry)
- bismuth vanadate (a pigment)
- indanthrone blue (a pigment)
- SA (styrene acrylic - used as a glue for paper applications)
- HALS (hindered amine light stabilisers - used in plastics) and
- UV (ultraviolet light) filters for skin care products.In the markets where the Commission identified competition concerns one or both parties held significant market shares even before the transaction and the proposed takeover would lead to further strengthening of these positions.
Divestments
To resolve these competition concerns, BASF proposed to divest DMA3 production assets at Ludwigshafen (Germany), Ciba’s entire EEA synthetic dry strength agent business and Ciba’s global bismuth vanadate business.
Regarding indanthrone blue, BASF agreed to transfer Ciba’s know-how of the finishing line, all supply contracts, customer lists and inventories.
For SA, BASF agreed to divest Ciba’s SA business (and the PVAc - polyvinyl acetate and AA ? all acrylate businesses) in the EEA at Kaipiainen (Finland).
For HALS, BASF committed to divest Ciba’s entire Chimassorb 119 FL business, including the Chimassorb 119 FL production assets, relevant know-how and customer lists.
For UV filters, BASF committed to conclude a UV Filter Licence Agreement, giving third party access to the technology behind Tinosorb S (a UV filter patented and currently solely produced by Ciba).
Following a market investigation, the Commission concluded that the divested businesses would be viable and that the commitments would resolve all identified competition concerns.
BASF to sell China
process catalysts site to Sud-Chemie
BASF today announced that it has signed a definitive agreement to
sell its catalysts manufacturing facility in Nanjing, China, to Sud-Chemie
AG, a
worldwide leading speciality chemical company for catalysts and
adsorbents headquartered in Munich, Germany. The facility is
independent from BASF’s main Verbund site in Nanjing.
Both companies have agreed not to disclose financial details of
the transaction.
The facility produces more than 30 different types of syngas
catalysts, including products for manufacturing ammonia and
methanol. A transition plan for the approximately 400 employees
working at the process catalyst site is being developed together
with Sud-Chemie. Despite the sale of the Nanjing catalyst site,
BASF remains committed to being the global leader in the process
catalysts industry and the preferred catalysts supplier for its
customers.
“China
will continue to be a major focus of our process catalysts
business. Because BASF has an extensive platform in China, we see
our best growth opportunities in leveraging BASF’s assets to capitalize on the
growing Chinese catalyst market,” said Wilfried Seyfert, Group Vice
President, Process Catalysts and Technologies. “This catalysts site did not
represent a strong fit with BASF’s other operations in China. We
therefore determined that our best strategy was to sell the site
as part of BASF’s ongoing efficiency and
restructuring programs.”
Dr. Gunter von Au,
Chairman of the Managing Board of Sud-Chemie AG, commented: “Acquiring syngas catalyst
production in Nanjing is an important strategic cornerstone for
the expansion of Sud-Chemie in China and expanding our catalyst
business in Asia. With the new site, we strengthen not only our
market position in the Chinese growth market for catalysts for
converting coal into high quality chemical products, but we also
consolidate our position as worldwide technology and market
leader in this area of business.”
About BASF’s Catalysts division
BASF’s Catalysts division is the world’s leading supplier of
environmental and process catalysts. The group offers exceptional
expertise in the development of technologies that protect the air
we breathe, produce the fuels that power our world and ensure
efficient production of a wide variety of chemicals, plastics,
adsorbents and other products.
Süd-Chemie is a highly-innovative, listed, specialty chemicals company headquartered in Munich. With its two divisions of Adsorbents 吸着剤 and Catalysts, the Süd-Chemie Group, which has around 6,500 employees, generates total sales of almost 1.2 billion euros. Süd-Chemie holds an extremely strong position on global markets, almost 80 percent of Group sales being realised with customers outside Germany. It systematically exploits the potential offered by fast-growing regions, notably in Southeast Asia and the Middle East.
The starting material for products manufactured by the Adsorbents Division is a clay mineral known as bentonite. This clayey rock binds materials dissolved in water or other liquids and can be chemically refined to create versatile adsorbents and additives.
水を吸うと自らの体積の10倍以上に膨張し、さらに多量の水と混合すると強力な粘性を発揮する。しかも、長時間おいても沈殿せず、無機物だから公害の心配がない。こんな不思議な粘土、それがベントナイトです。
他の鉱物には無い、こうしたユニークな性質によって、建築・土木工事の施工や鉱業製品の製造に不可欠な素材として、化粧品や医療品などの原料として、さらには小動物の排泄物を処理するペット砂として、幅広く利用されています。
In March 2003, SABIC and Süd-Chemie AG formed a partnership for the acquisition of Scientific Design Company Inc. from Linde AG. Under this changed ownership, Scientific Design remains an independent entity and continues to license its processes, provide engineering services and sell catalysts to its clients worldwide. SABIC and Süd-Chemie manage Scientific Design Company Inc. through a fifty-fifty joint venture. http://www.knak.jp/big/sabic-2.htm#sd
Süd-Chemie
| 部門 | 売上高 (百万ユーロ) |
従業員 | |
| Absorbents | 702 | 3,836人 | Absorbents
and additives Perofrmance packaging Foundry products and specialty resins Water treatment |
| Catalysts | 490 | 2,271 | Catalytic
technologies Energy and environment |
| Total | 1,191 | 6,513 |
BASF to close the Styropor (EPS) plant and further adjust its production services at its Tarragona site
BASF will shut down the Styropor® plant (EPS, expandable polystyrene) at its site in Tarragona, Spain. The closure is scheduled for August 2009. As a direct consequence of the plant closure and due to the current downturn in BASF's key markets in Spain, the company will also adjust the structure of production services in Tarragona. In total, 85 BASF employees working in production and related services such as maintenance, engineering and logistics are affected by these measures. This amounts to 9 percent of all jobs of BASF Española S.L..
The Styropor plant has become uneconomical due to its relatively small production capacity which has resulted in an unfavorable cost-structure. “The decision to close the Styropor plant does not mean that BASF will retreat from the Iberian EPS market," said Giorgio Greening, head of the Global Business Unit Foams. "BASF will continue to supply the region with high-quality EPS from Ludwigshafen, Germany and intends to defend its market share”.
BASF to reduce
polystyrene capacity in Europe by about 15 percent
One production plant in
Ludwigshafen to be permanently closed
Personnel to be transferred to
other functions within the company
Effective June 30, 2009, BASF will close one polystyrene plant at
the Ludwigshafen site. This will reduce BASF’s annual production capacity for
the standard plastic polystyrene in Europe by
80,000 to 540,000 metric tons, what comes up to a capacity
reduction of about 15 percent.
The main reason for the shutdown is the decrease in demand for
Polystyrene. The affected plant, which has been out of operation
since mid-April, will be dismantled. Personnel working at this
plant will transfer to other positions within the company.
Polystyrene will continue to be produced by BASF in Ludwigshafen
but it will serve primarily for the manufacture of the two BASF
insulation products Styrodur(R)C and Neopor(R)
(extrusion-based).
In the future, orders for Polystyrene from European customers who
had previously been supplied from Ludwigshafen will be filled
mainly from the plant at BASF’s Verbund site in Antwerp,
Belgium.
BASF reorganizes its Petrochemicals Division
BASF reorganizes its Petrochemicals division effective July 1, 2009. The future organization consists of four (formerly six) business units. The optimized organizational structures will lead to higher efficiency and effectiveness and will open up potentials to even better serve customers´ needs. Customers will benefit from a reduced number of interfaces and a broader portfolio of the respective business units. The new clustering of businesses also comes along with new business opportunities as well as synergy effects out of the BASF Verbund.
The new organizational setup is based on a thorough analysis of the market and economic situation, which has fundamentally changed over the last years. Exemplary for this change are the important BASF investments in Nanjing (China) and Port Arthur (USA).
The details of the reorganization are as follows:
| 2008/1/1から 以下の6セグメントに変更 |
 |
Alkylene Oxides and Glycols、Cracker Products、Industrial Gases、Specialty Monomers、
Standard Monomers、Plasticizers、Solvents
2009-07-06
BASF specifies restructuring plans
*23 of 55 acquired production sites worldwide under review
*Synergies of at least Euro400 million per year expected
*Fair and transparent decisions
BASF has finalized its plans for the integration of Ciba Holding
AG, which it acquired in April 2009. Under the plans, former Ciba
businesses are to be integrated into the operating divisions in BASF’s Performance Products segment where their potential can best be
realized and developed. The integration will involve extensive
restructuring measures that BASF expects to generate synergies of at
least Euro400 million per year from 2012 onward. By the end of
2010, savings of approximatelyEuro300 million are to be achieved.
At the same time, the integration process is expected to entail
cash costs totaling approximately Euro550 million, about Euro150
million thereof in 2009. BASF will report details of non-cash
integration costs as part of its second-quarter interim reporting
on July 30, 2009.
BASF aims to grow above
market: Asia Pacific sales to double by 2020
*Asia Pacific Strategy 2020 targets growth of two percentage
points above market
*Earn premium on cost of capital
*70 percent of sales to be manufactured locally
*Headcount to increase by at least 5,000
*Investments of ?2 billion planned between 2009 and 2013
*Efficiency improvements to save at least ?100 million annually
by 2012
BASF today outlined its Strategy 2020 for Asia Pacific. Through
2020, BASF aims to grow on average two percentage points faster
than the Asia Pacific chemical market each year. With expected
market growth of 4 to 5 percent per year, this would double
regional sales by 2020 while earning a premium on cost of
capital.
This ambitious strategy is based on growth and new business
initiatives. Under its new strategy, BASF will initially target five key
growth industries in the region, will increase headcount by at
least 5,000 from a current figure of approximately 15,000, and
plans to generate 70 percent of regional sales from local
production. At the same time, the company will invest Euro2
billion in the region between 2009 and 2013, and aims to create
efficiency improvements that are expected to save at least
Euro100 million annually by 2012.
“BASF
has established its position as the leading chemical company
owing to its long-standing commitment to the Asia Pacific region.
The Asian growth markets will continue to provide attractive
opportunities, and our Strategy 2020 will help us to realize
them,” said Dr. Martin Brudermuller,
member of the Board of Executive Directors of BASF SE,
responsible for Asia Pacific. “The current economic situation
does not change our positive expectations of the long-term
potential of these dynamic markets.”
Investments of
Euro2 billion between 2009 and 2013
To support the goal of producing 70 percent of its sales within
the Asia Pacific region, BASF plans to invest Euro2
billion between 2009 and 2013. This amount includes BASF’s 50 percent share of the $1.4
billion expansion of its integrated chemical production joint
venture in Nanjing, China, which was approved by the
national government in July 2009. In Chongqing, China, BASF is in
the planning phase for a 400,000 ton/year plant for
MDI, a
precursor for polyurethanes. BASF and the Chongqing authorities
aim for mechanical completion of the plant by the end of 2013 and
commercial operation by early 2014. Final approvals of the
project by Chinese regulators are expected in 2009, and
subsequently the BASF Board of Executive Directors plans to
approve the investment in the first quarter of 2010.
Five key customer industries, new geographic markets
In Asia Pacific, BASF will organize its sales efforts around key
industries in order to grow faster than the market. The company
has established an initial set of industry target groups where it
intends to become a preferred supplier, including the automotive,
construction, packaging, paint and coatings, and pharmaceuticals
industries.
By looking closely at the value chains in these key industries,
BASF will better understand its customers’
needs and will be
better positioned to provide products and solutions based on BASF’s global knowledge and resources.
A few examples of chemical innovations from BASF already
introduced for these industries include engineering
plastics for lightweight cars, insulation systems and concrete
admixtures for energy-efficient housing, biodegradable packaging
materials, environmentally friendly paint ingredients, and
advanced intermediates for pharmaceutical production.
Already present in 15 countries in the region, with significant
operations in China, Japan, Korea, Malaysia and India, BASF will
also actively seek opportunities to support rapidly developing
customer markets in relatively untapped locations, including
Vietnam and inland China.
Larger local team, enhanced R&D capabilities
To achieve its goals, BASF will implement an enhanced development
plan to strengthen its existing local talent base. By 2020, BASF
expects to increase its headcount in Asia Pacific by at least
5,000. In its two challenging growth markets, China and India,
BASF has set up dedicated recruitment centers to manage the
increase in hiring. The company will double the number of
employees in research and development by 2020, especially at its
two major R&D clusters in China and India. Currently, BASF
has 300 employees working in R&D at 15 sites in Asia Pacific.
“Local
innovation and local production are driving business growth in
this region. We therefore want to develop new applications,
products and solutions together with our customers in Asia,
adapted for Asian needs, and then serve local markets primarily
through our sites and our talent in the region,”
continued
Brudermuller.
Operating efficiencies with site optimization
BASF plans to reduce costs by at least ?100 million annually by
2012, increasing the efficiency of its existing operations. An
important aspect of this effort is the company’s Site Optimization Project, which
aims to increase capacity through debottlenecking production and
by exploiting technical synergies, for example in production
processes or across sites. All measures implemented under this
project are expected to recoup their costs within one year.
Site optimization in Asia Pacific is ongoing at the company’s integrated production sites in
Kuantan, Malaysia, and Nanjing, China, as well as in Yeosu, Korea
and other production sites in the region.
2009-10-10 CCR
BASF Plans MDI Plant in Chongqing
BASF plans to build a MDI (diphenylmethane diisocyanate) plant in Chongqing. BASF and Chongqing authorities aim for mechanical completion of the 400 000 t/a MDI plant by 2013 and commercial operation by 2014. Final approvals of the project by Chinese regulators are expected in 2009, and subsequently the BASF Board of Executive Directors plans to approve the investment in the first quarter of 2010 after finalizing all necessary agreements regarding raw materials and utilities supply and integration.
BASF announces its
intention to cease activities in Feluy, Belgium
* Exit from maleic anhydride production intended by end 2009
* 133 employees impacted, alternative employment options to be
evaluated
BASF Antwerpen N.V. today announced its intention to close its 115,000 annual
tons maleic anhydride (MA) production facility by the end of 2009 and to withdraw all BASF
activities from its site in Feluy, Belgium. BASF employs 133 people at the
Feluy site, which is part of BASF Antwerpen N.V. “Information and consultation
procedures have been initiated today with the works council. We
will start negotiations with the union representatives as soon as
possible to ensure socially acceptable solutions for all
employees who could be affected and to evaluate alternative
employment options should the closing be effectively decided,”
said Wouter De
Geest, CEO of BASF Antwerpen N.V.
BASF’s MA business is suffering from
unsatisfactory profitability due to overcapacity and resulting
low margins together with the effects of the current economic
crisis. Optimization measures implemented in Feluy over the past
years have not been sufficient to secure a sustainably
competitive cost structure. “A withdrawal from maleic anhydride
production in Feluy would help us to focus on our core
intermediates businesses and Verbund value chains such as
butanediol and derivatives, as well as polyalcohols,”
said Dr. Tom
Witzel, Group Vice President Diols & Polyalcohols Europe of
BASF’s Intermediates division.
MA serves mainly as a building block to produce unsaturated
polyester resins. These resins are widely used as composite
materials, particularly in shipbuilding, construction and
automobile industries. MA is also used for many other
applications, like water-soluble polymers and lubricants.
About BASF Antwerpen N.V.:
BASF Antwerpen N.V. is a wholly owned subsidiary of BASF SE. The
site in the northernmost part of the port of Antwerp is the
biggest integrated chemical complex in Belgium and the second
largest Verbund site in the BASF Group. The BASF site in Antwerp
produces chemicals, fertilizers, plastics and performance
chemicals in more than 50 plants. BASF Antwerpen N.V. has more
than 3,500 employees and posted sales of Euro 6.2 billion in
2008. More information is available at www.basf.be.
2005年 FeluyでBDO生産停止
BASF Shown Styrene Escape
Route by Dow as Buyout Firms Close In
BASF SE, seeking to end an almost three-year quest to sell
unwanted styrene assets, will look to emulate Dow Chemical Co.
after its U.S. rival
attracted bids from buyout firms to a competing business.
Interest in acquisitions is picking up in the chemical industry,
a trend borne out by Dow getting private equity approaches for
the Styron Inc. unit, said Johan van den Arend Schmidt, a
strategist at PricewaterhouseCoopers. Dow aims to sell Styron by
the end of March after an eight-month process.
Selling styrene assets would accelerate BASF’s move away from less-profitable
commodity products used in cutlery and televisions as Middle East
rivals expand capacity in that market. Chief Executive Officer
Juergen Hambrecht, who retires next year, has made acquisitions
to expand in markets for catalysts used in car exhausts and
cosmetic additives.
“The
deal market is coming back in a strong way in the chemical
sector,” said London-based Van den Arend
Schmidt. “There’s a lot of interest
in chemical assets, including for instance Styron. It puts BASF in a very good
position. If they want to do something, they can use 2010 to do
it.”
After holding
second-round bids last month, Midland-based Dow is opening Styron’s books for further due diligence
to whittle down the number of remaining private equity suitors,
said a person with knowledge of the situation, who declined to be
identified because the sale process is private. Styron generates
$5 billion in sales, and employs 1,500. The U.S. company values
the business at $1 billion to $2 billion. Spokesman Bob Plishka
declined to comment on the sale process.
BASF’s styrenics unit generates 3
billion euros ($4.2 billion) in sales and employs 1,600. It may
fetch 1 billion euros ($2.1 billion) to 1.5 billion euros, said
Sylvia Quandt Research analyst Harald Gruber.
Sharing Suitors
For BASF, finding a buyer would mean avoiding a prolonged exit
via a partnership agreement, which analysts view as a consolation
move. Talks are under way with a potential partner for a styrene
joint venture, as a prelude to exiting the market, BASF said in
November. Spokesman Michael Grabicki said there’s “nothing new to report”
on the matter.
“There
is a good chance some of the bidders for Styron may also be
attracted to BASF’s styrene business,”
Gruber said.
About 50 buyout firms have invested in the chemical industry in
the past decade. The largest deals include Apollo Management LP’s purchase of General Electric Co.’s silicone division in 2006 for
about $3.8 billion.
U.S. and European styrene makers face competition from Middle
East petrochemical suppliers keen to diversify away from refining
and raw materials. International Petroleum Investment Co. of Abu
Dhabi last year acquired Nova Chemicals Corp. of Canada. Saudi
Basic Industries Corp. aims to become the world leader in
chemicals by 2020. Antitrust rules could prevent European rivals
Total SA and Ineos Nova LLC from bidding.
Investor ‘Relief’
Dow and BASF have
increased prices for polystyrene in the past two months, moves
timed with increases in the cost of benzene. Higher raw-material
costs and the recession that clipped orders from construction,
auto and consumer-goods clients have damped margins and the value
of styrene plants.
Europe’s polystyrene market shrank about
15 percent over the last two years, yet capacity cuts mean the
region’s suppliers should “earn money again this year,”
said Martin
Wiesweg, an analyst at chemical consultant CMAI in Dusseldorf. He
predicts a small rebound in 2010.
“If
BASF would finally be able to sell this business, it would be a
relief,” said Boris Schakowski, a fund
manager at Union Investment in Frankfurt, who holds BASF shares. “The business doesn’t live up to BASF standards in
terms of profitability. Still, BASF might not be willing to sell
it below its value.”
Credit Suisse’s John McNulty “conservatively”
estimates Dow’s Styron assets could fetch as
much as five times operating profit. Dow paid 10 times earnings
when it bought additives maker Rohm & Haas for $15.4 billion.
Hambrecht Legacy
Since taking the helm in 2003, Hambrecht has almost doubled sales
to more than 60 billion euros. Profit has tripled to 2.9 billion
euros as the 63-year-old chemist, born in the industrial Swabian
region of southern Germany, made acquisitions to diversify.
Hambrecht plans to step down in April 2011.
“Selling
styrene may be Hambrecht’s last billion-euro- deal, and he
may want to retire with this chapter closed too,”
said Silvia’s Gruber. “He’s not the kind of person who likes
to leave things unfinished.”
BASF starts up new plant to increase polyisobutene (PIB) capacity
BASF has started up a new plant for the production of low-molecular-weight, highly reactive polyisobutene (HR PIB) at its site in Ludwigshafen, Germany, thus increasing its annual capacity by 25,000 metric tons to 40,000 metric tons. The polymer, marketed worldwide under the Glissopal® trademark, is an important intermediate product for the manufacture of additives for fuels and lubricants.
The present increase in capacity is the second significant one within the last two years. In April 2008 BASF increased its annual capacity for Glissopal® at its site in Antwerp, Belgium by 25,000 metric tons to 100,000 metric tons.
“In taking this step, we are strengthening our polyisobutene production here at Ludwigshafen. It also shows once again the benefits of our Verbund production network. Integration in the Verbund reduces the number of shipments between different sites, and hence the amount of traffic on our roads”, says Hans W. Reiners, head of BASF’s Performance Chemicals division.
Ralf Spettmann, head of the Automotive and Refinery Chemicals business unit adds: “With this investment, we are adapting our capacity sustainably to the steadily increasing demand and continue to be a reliable partner for our customers.”
The low molecular weight products are marketed under the Glissopal trademark. The number-average molecular weight (Mn) of the indivi are free of chlorine, and they are miscible in all proportions with mineral oils and poly-a-olefins. Because of the special process highly reactive, with the result that the yield is high when they react with maleic anhydride to form polyisobutenyl succinic anhyd reacting PIBSA with polyamines.
BYC will also develop the cracker's C4 chain with the manufacture of butadiene (BD) and isobutene, with derivatives including the plasticizer alcohol 2-propylheptanol and highly reactive polyisobutylene (HR-PIB), which is used in the manufacture of fuels and lubricants.
BASF-YPCの増設計画の内容
エチレン: 600千トンから740千トンへ増強
EO(新設): 80千トン
高吸水性樹脂(新設): 60千トン
非イオン性界面活性剤(新設): 60千トン
ブタジエン抽出(新設): 100千トン~120千トン
イソブテン(新設): 80千トン
ポリイソブテン(新設): 50千トン